Utility and diagnostic accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial fine-needle aspiration cytology of mediastinal lesions: Saudi Arabian experience
- PMID: 25191512
- PMCID: PMC4141359
- DOI: 10.4103/1742-6413.137760
Utility and diagnostic accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial fine-needle aspiration cytology of mediastinal lesions: Saudi Arabian experience
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study is to evaluate the cytological accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial fine-needle aspiration (EBUS-TFNA) of the mediastinal mass/nodular lesions.
Study design: Over 3½ years from inception at King Khalid University Hospital, a retrospective analysis of the cytological diagnoses of all the EBUS-TFNA procedures performed in 80 patients who had mediastinal mass/nodular enlargement. Cytology results were reviewed and correlated with the histologic follow-up.
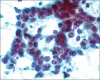
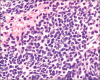
Results: Of the 80 patients who underwent EBUS-TFNA, 15 cases (18.75%) were positive for malignancy, 48 cases (60%) negative for malignancy and 17 cases (21.25%) unsatisfactory. Of the 48 cases, which were negative for malignancy, 24 (50%) cases were of granulomatous inflammation. The overall diagnostic yield of our EBUS-TFNA specimen was 78.75%. Forty-seven cases (58.75%) of 80 cases had histological follow-up biopsies. Among them, 32 cases (68%) had the same cytological and histological diagnosis and 15 cases (31.09%) had discordance between the cytology and the follow-up histological diagnosis. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for diagnosing granulomas by EBUS-TFNA are 77%, 82%, 83%, and 75% and for diagnosing malignancy are 71%, 100%, 100%, and 82%, respectively.
Conclusion: Preliminary results show that cytological samples obtained through EBUS-TFNA are accurate and specific in making a diagnosis of the mediastinal mass/nodular lesions. Its optimum use depends on the effective collaboration between the cytotechnologist, pathologist, and the bronchoscopist.
Keywords: Cytology; endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial fine-needle aspiration; fine-needle aspiration.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Utility of endoscopic ultrasound-guided transbronchial fine-needle cytology in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis: A Saudi experience.Cytojournal. 2014 Dec 3;11:31. doi: 10.4103/1742-6413.146118. eCollection 2014. Cytojournal. 2014. PMID: 25558271 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of endobronchial ultrasound-guided-fine-needle aspiration and additional value of cell block in the diagnosis of mediastinal granulomatous lymphadenopathy.Cytojournal. 2015 Sep 22;12:20. doi: 10.4103/1742-6413.165947. eCollection 2015. Cytojournal. 2015. PMID: 26445590 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cytology in endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration: A study of 813 cases focusing on diagnostic yield, an analysis of misdiagnosed cases and diagnostic accordance rate of cytological subtyping.Diagn Cytopathol. 2021 Jan;49(1):119-126. doi: 10.1002/dc.24608. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Diagn Cytopathol. 2021. PMID: 32894657 Free PMC article.
-
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) in diagnosis of mediastinal lesions.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2018 May 14;16(2):eAO4094. doi: 10.1590/S1679-45082018AO4094. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2018. PMID: 29768518 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of endobronchial ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspirations (EBUS-FNA): correlation with adequacy and histologic follow-up.Cancer Cytopathol. 2014 Jan;122(1):23-32. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21350. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014. PMID: 24127207
Cited by
-
Utility of endoscopic ultrasound-guided transbronchial fine-needle cytology in the diagnosis of sarcoidosis: A Saudi experience.Cytojournal. 2014 Dec 3;11:31. doi: 10.4103/1742-6413.146118. eCollection 2014. Cytojournal. 2014. PMID: 25558271 Free PMC article.
-
Utility and safety of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in patients with mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy: Western region experience.Ann Thorac Med. 2018 Apr-Jun;13(2):92-100. doi: 10.4103/atm.ATM_317_17. Ann Thorac Med. 2018. PMID: 29675060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skov BG, Baandrup U, Jakobsen GK, Kiss K, Krasnik M, Rossen K, et al. Cytopathologic diagnoses of fine-needle aspirations from endoscopic ultrasound of the mediastinum: Reproducibility of the diagnoses and representativeness of aspirates from lymph nodes. Cancer. 2007;111:234–41. - PubMed
-
- Jacob-Ampuero MP, Haas AR, Ciocca V, Bibbo M. Cytologic accuracy of samples obtained by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital. Acta Cytol. 2008;52:687–90. - PubMed
-
- Groth SS, Whitson BA, D’Cunha J, Maddaus MA, Alsharif M, Andrade RS. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of mediastinal lymph nodes: A single institution's early learning curve. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;86:1104–9. - PubMed
-
- Alsharif M, Andrade RS, Groth SS, Stelow EB, Pambuccian SE. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial fine-needle aspiration: The University of Minnesota experience, with emphasis on usefulness, adequacy assessment, and diagnostic difficulties. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;130:434–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

