Radioembolization of hepatic lesions from a radiobiology and dosimetric perspective
- PMID: 25191640
- PMCID: PMC4137387
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00210
Radioembolization of hepatic lesions from a radiobiology and dosimetric perspective
Abstract
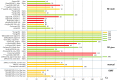
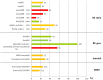
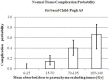
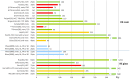
Radioembolization (RE) of liver cancer with (90)Y-microspheres has been applied in the last two decades with notable responses and acceptable toxicity. Two types of microspheres are available, glass and resin, the main difference being the activity/sphere. Generally, administered activities are established by empirical methods and differ for the two types. Treatment planning based on dosimetry is a prerogative of few centers, but has notably gained interest, with evidence of predictive power of dosimetry on toxicity, lesion response, and overall survival (OS). Radiobiological correlations between absorbed doses and toxicity to organs at risk, and tumor response, have been obtained in many clinical studies. Dosimetry methods have evolved from the macroscopic approach at the organ level to voxel analysis, providing absorbed dose spatial distributions and dose-volume histograms (DVH). The well-known effects of the external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), such as the volume effect, underlying disease influence, cumulative damage in parallel organs, and different tolerability of re-treatment, have been observed also in RE, identifying in EBRT a foremost reference to compare with. The radiobiological models - normal tissue complication probability and tumor control probability - and/or the style (DVH concepts) used in EBRT are introduced in RE. Moreover, attention has been paid to the intrinsic different activity distribution of resin and glass spheres at the microscopic scale, with dosimetric and radiobiological consequences. Dedicated studies and mathematical models have developed this issue and explain some clinical evidences, e.g., the shift of dose to higher toxicity thresholds using glass as compared to resin spheres. This paper offers a comprehensive review of the literature incident to dosimetry and radiobiological issues in RE, with the aim to summarize the results and to identify the most useful methods and information that should accompany future studies.
Keywords: 90Y-microspheres; dosimetry; liver tumors; radiobiology; radioembolization.
Figures
References
-
- Therasphere® by BTG (http://www.therasphere.com). Available from: http://www.therasphere.com/physicians-package-insert/package-insert-eu-e...
-
- SIR-Spheres Yttrium-90 Microspheres [Package Insert] Lane Cove: Sirtex Medical; (2004). Available from: http://www.sirtex.com/files/US20Package20Insert1.pdf
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

