Importance of fatty acid compositions in patients with peripheral arterial disease
- PMID: 25191963
- PMCID: PMC4156400
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107003
Importance of fatty acid compositions in patients with peripheral arterial disease
Abstract
Objective: Importance of fatty acid components and imbalances has emerged in coronary heart disease. In this study, we analyzed fatty acids and ankle-brachial index (ABI) in a Japanese cohort.
Methods: Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) was diagnosed in 101 patients by ABI ≤0.90 and/or by angiography. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors and components of serum fatty acids were examined in all patients (mean age 73.2±0.9 years; 81 males), and compared with those in 373 age- and sex-matched control subjects with no evidence of PAD.
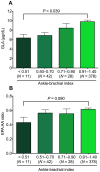
Results: The presence of PAD (mean ABI: 0.71±0.02) was independently associated with low levels of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) (OR: 0.90; 95% CI: 0.85-0.96; P = 0.002), eicosapentaenoic acid∶arachidonic acid (EPA∶AA) ratio (OR: 0.38; 95% CI: 0.17-0.86; P = 0.021), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (OR: 0.97; 95% CI: 0.96-0.98; P<0.0001), and with a high hemoglobin A1c level (OR: 1.34; 95% CI: 1.06-1.69; P = 0.013). Individuals with lower levels of GLA (≤7.95 µg/mL) and a lower EPA∶AA ratio (≤0.55) had the lowest ABI (0.96±0.02, N = 90), while the highest ABI (1.12±0.01, N = 78) was observed in individuals with higher values of both GLA and EPA∶AA ratio (P<0.0001).
Conclusion: A low level of GLA and a low EPA∶AA ratio are independently associated with the presence of PAD. Specific fatty acid abnormalities and imbalances could lead to new strategies for risk stratification and prevention in PAD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship Between Serum Eicosapentaenoic Acid to Arachidonic Acid Ratio and Atherosclerotic Risk Factors in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease.Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2021 Feb;55(2):112-116. doi: 10.1177/1538574420967130. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2021. PMID: 33073735
-
Reduced plasma eicosapentaenoic acid-arachidonic acid ratio in peripheral artery disease.Angiology. 2013 Feb;64(2):112-8. doi: 10.1177/0003319712437031. Epub 2012 Feb 26. Angiology. 2013. PMID: 22371626
-
Association between estimated glomerular filtration rate and peripheral arterial disease.J Cardiol. 2015 Nov;66(5):430-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Apr 13. J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25881730
-
Risk factors and haemodynamic variables in patients with low toe-brachial index but normal ankle-brachial index.Atherosclerosis. 2019 Oct;289:21-26. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.08.005. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Atherosclerosis. 2019. PMID: 31446210
-
Relation of omega-3 fatty acid and C-reactive protein to peripheral artery disease in patients with coronary artery disease.Heart Vessels. 2014 Jul;29(4):449-55. doi: 10.1007/s00380-013-0384-4. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Heart Vessels. 2014. PMID: 23801460
Cited by
-
Effects of sarpogrelate, eicosapentaenoic acid and pitavastatin on arterioslcerosis obliterans-related biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes (SAREPITASO study).Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018 Sep 18;14:225-232. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S171143. eCollection 2018. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 30271161 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation: a possible therapeutic target for skeletal muscle lipotoxicity in peripheral artery disease myopathy.EXCLI J. 2024 Apr 23;23:523-533. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7004. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 38741727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of γ-linolenic acid, Vitis vinifera extract, and acetyl-L-carnitine combination therapy for improving arterial stiffness in Korean adults: Real-world evidence.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2023 Sep;25(9):880-888. doi: 10.1111/jch.14708. Epub 2023 Aug 22. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2023. PMID: 37608640 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosapentaenoic Acid Level Predicts Long-Term Survival and Cardiovascular or Limb Event in Peripheral Arterial Disease.Ann Vasc Dis. 2024 Jun 25;17(2):135-141. doi: 10.3400/avd.oa.23-00079. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Ann Vasc Dis. 2024. PMID: 38919321 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of eicosapentaenoic acid/arachidonic acid ratio (EPA/AA) in adult patients with congenital heart disease.Heart Vessels. 2017 Dec;32(12):1513-1522. doi: 10.1007/s00380-017-1015-2. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Heart Vessels. 2017. PMID: 28681101
References
-
- Criqui MH, Langer RD, Fronek A, Feigelson HS, Klauber MR, et al. (1992) Mortality over a period of 10 years in patients with peripheral arterial disease. N Engl J Med 326: 381–386. - PubMed
-
- Selvin E, Erlinger TP (2004) Prevalence of and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2000. Circulation 110: 738–743. - PubMed
-
- Ohnishi H, Sawayama Y, Furusyo N, Maeda S, Tokunaga S, et al. (2010) Risk factors for and the prevalence of peripheral arterial disease and its relationship to carotid atherosclerosis: the Kyushu and Okinawa Population Study (KOPS). J Atheroscler Thromb 17: 751–758. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara T, Saitoh S, Takagi S, Ohnishi H, Ohata J, et al. (2004) Prevalence of asymptomatic arteriosclerosis obliterans and its relationship with risk factors in inhabitants of rural communities in Japan: Tanno-Sobetsu study. Atherosclerosis 177: 83–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

