Evaluation of antithrombotic activity of thrombin DNA aptamers by a murine thrombosis model
- PMID: 25192011
- PMCID: PMC4156426
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107113
Evaluation of antithrombotic activity of thrombin DNA aptamers by a murine thrombosis model
Abstract
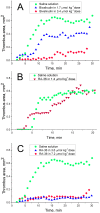
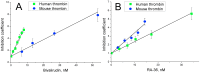
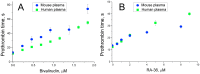
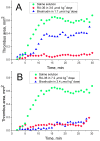
Aptamers are nucleic acid based molecular recognition elements with a high potential for the theranostics. Some of the aptamers are under development for therapeutic applications as promising antithrombotic agents; and G-quadruplex DNA aptamers, which directly inhibit the thrombin activity, are among them. RA-36, the 31-meric DNA aptamer, consists of two thrombin binding pharmacophores joined with the thymine linker. It has been shown earlier that RA-36 directly inhibits thrombin in the reaction of fibrinogen hydrolysis, and also it inhibits plasma and blood coagulation. Studies of both inhibitory and anticoagulation effects had indicated rather high species specificity of the aptamer. Further R&D of RA-36 requires exploring its efficiency in vivo. Therefore the development of a robust and adequate animal model for effective physiological studies of aptamers is in high current demand. This work is devoted to in vivo study of the antithrombotic effect of RA-36 aptamer. A murine model of thrombosis has been applied to reveal a lag and even prevention of thrombus formation when RA-36 was intravenous bolus injected in high doses of 1.4-7.1 µmol/kg (14-70 mg/kg). A comparative study of RA-36 aptamer and bivalirudin reveals that both direct thrombin inhibitors have similar antithrombotic effects for the murine model of thrombosis; though in vitro bivalirudin has anticoagulation activity several times higher compared to RA-36. The results indicate that both RA-36 aptamer and bivalirudin are direct thrombin inhibitors of different potency, but possible interactions of the thrombin-inhibitor complex with other components of blood coagulation cascade level the physiological effects for both inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
G-Quadruplex Aptamers to Human Thrombin Versus Other Direct Thrombin Inhibitors: The Focus on Mechanism of Action and Drug Efficiency as Anticoagulants.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(21):2230-44. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160517120126. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27183984 Review.
-
Antithrombotic but not anticoagulant activity of the thrombin-binding RNA aptamer Apta-1.Br J Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;182(6):1358-1376. doi: 10.1111/bph.17382. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39653034
-
[Clinical use of a new class of anticoagulant drugs: the direct thrombin inhibitors].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2006 Nov;7(11):739-46. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2006. PMID: 17216915 Review. Italian.
-
Module-activity relationship of G-quadruplex based DNA aptamers for human thrombin.Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(38):4836-43. doi: 10.2174/09298673113206660283. Curr Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24083606
-
Bivalirudin: a direct thrombin inhibitor.Clin Ther. 2002 Jan;24(1):38-58. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(02)85004-4. Clin Ther. 2002. PMID: 11833835 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer Conjugated RNA/DNA Hybrid Nanostructures Designed for Efficient Regulation of Blood Coagulation.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2709:277-286. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3417-2_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37572288 Free PMC article.
-
The Evaluation of Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics of Anti-thrombin DNA Aptamer RA-36.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 14;8:922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00922. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29311929 Free PMC article.
-
G-Quadruplex-Forming Aptamers-Characteristics, Applications, and Perspectives.Molecules. 2019 Oct 21;24(20):3781. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203781. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31640176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locking and Unlocking Thrombin Function Using Immunoquiescent Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles with Regulated Retention In Vivo.Nano Lett. 2022 Jul 27;22(14):5961-5972. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c02019. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Nano Lett. 2022. PMID: 35786891 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplex-based aptamers against protein targets in therapy and diagnostics.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt B):1429-1447. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.11.027. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27865995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Monroe DM, Hoffman M (2006) What does it take to make the perfect clot? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26: 41–48. - PubMed
-
- Davie EW, Fujikawa K, Kisiel W (1991) The coagulation cascade: initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry 30: 10363–10370. - PubMed
-
- Nutescu EA, Shapiro NL, Chevalier A, Amin AN (2005) A pharmacologic overview of current and emerging anticoagulants. Cleve Clin J Med 72: S2–S6. - PubMed
-
- De Cristofaro R, De Candia E (2003) Thrombin domains: structure, function and interaction with platelet receptors. J Thromb Thrombolysis 15: 151–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

