Diagnostic accuracy of computer-aided detection of pulmonary tuberculosis in chest radiographs: a validation study from sub-Saharan Africa
- PMID: 25192172
- PMCID: PMC4156349
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106381
Diagnostic accuracy of computer-aided detection of pulmonary tuberculosis in chest radiographs: a validation study from sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract
Background: Chest radiography to diagnose and screen for pulmonary tuberculosis has limitations, especially due to inter-reader variability. Automating the interpretation has the potential to overcome this drawback and to deliver objective and reproducible results. The CAD4TB software is a computer-aided detection system that has shown promising preliminary findings. Evaluation studies in different settings are needed to assess diagnostic accuracy and practicability of use.
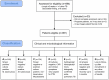
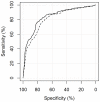
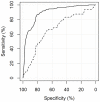
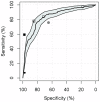
Methods: CAD4TB was evaluated on chest radiographs of patients with symptoms suggestive of pulmonary tuberculosis enrolled in two cohort studies in Tanzania. All patients were characterized by sputum smear microscopy and culture including subsequent antigen or molecular confirmation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) to determine the reference standard. Chest radiographs were read by the software and two human readers, one expert reader and one clinical officer. The sensitivity and specificity of CAD4TB was depicted using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, the area under the curve calculated and the performance of the software compared to the results of human readers.
Results: Of 861 study participants, 194 (23%) were culture-positive for M.tb. The area under the ROC curve of CAD4TB for the detection of culture-positive pulmonary tuberculosis was 0.84 (95% CI 0.80-0.88). CAD4TB was significantly more accurate for the discrimination of smear-positive cases against non TB patients than for smear-negative cases (p-value<0.01). It differentiated better between TB cases and non TB patients among HIV-negative compared to HIV-positive individuals (p<0.01). CAD4TB significantly outperformed the clinical officer, but did not reach the accuracy of the expert reader (p = 0.02), for a tuberculosis specific reading threshold.
Conclusion: CAD4TB accurately distinguished between the chest radiographs of culture-positive TB cases and controls. Further studies on cost-effectiveness, operational and ethical aspects should determine its place in diagnostic and screening algorithms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computer aided detection of tuberculosis on chest radiographs: An evaluation of the CAD4TB v6 system.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 26;10(1):5492. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62148-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32218458 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of Computer-Aided Detection of tuberculosis on Chest radiography among private sector patients in Pakistan.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 17;8(1):12339. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30810-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30120345 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided diagnostic accuracy of pulmonary tuberculosis on chest radiography among lower respiratory tract symptoms patients.Front Public Health. 2023 Oct 27;11:1254658. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1254658. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37965525 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis to compare the accuracy of GeneXpert, MODS and the WHO 2007 algorithm for diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Oct 30;13:507. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-507. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24172543 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking the diagnostic test accuracy of certified AI products for screening pulmonary tuberculosis in digital chest radiographs: Preliminary evidence from a rapid review and meta-analysis.Int J Med Inform. 2023 Sep;177:105159. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2023.105159. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Int J Med Inform. 2023. PMID: 37549498 Review.
Cited by
-
Low Prevalence of Active Tuberculosis among High-Risk Pregnant and Postpartum Women in Sweden: A Retrospective Epidemiological Cohort Study Using and Evaluating TST as Screening Method.Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul 18;2018:3153250. doi: 10.1155/2018/3153250. eCollection 2018. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 30154639 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of automated chest radiography reading software for tuberculosis screening among public- and private-sector patients.Eur Respir J. 2017 May 21;49(5):1602159. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02159-2016. Print 2017 May. Eur Respir J. 2017. PMID: 28529202 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of digital chest x-ray analysis with artificial intelligence software as a triage and screening tool in hospitalized patients being evaluated for tuberculosis in Lima, Peru.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024 Feb 7;4(2):e0002031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002031. eCollection 2024. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38324610 Free PMC article.
-
Parameter set for computer-assisted texture analysis of fetal brain.BMC Res Notes. 2016 Nov 25;9(1):496. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-2300-3. BMC Res Notes. 2016. PMID: 27887658 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis in Children.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2017 Aug;64(4):893-909. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2017.03.010. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28734517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Story A, Aldridge RW, Abubakar I, Stagg HR, Lipman M, et al. (2012) Active case finding for pulmonary tuberculosis using mobile digital chest radiography: an observational study. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 16: 1461–1467 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22981252 - PubMed
-
- Van't Hoog AH, Meme HK, Van Deutekom H, Mithika AM, Olunga C, et al. (2011) High sensitivity of chest radiograph reading by clinical officers in a tuberculosis prevalence survey. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 15: 1308–1314 Available: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/iuatld/ijtld/2011/00000015/0000001... - PubMed
-
- Den Boon S, White NW, Van Lill SWP, Borgdorff MW, Verver S, et al. (2006) An evaluation of symptom and chest radiographic screening in tuberculosis prevalence surveys. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 10: 876–882. - PubMed
-
- Van Cleeff M, Kivihya-Ndugga L, Meme H, Odhiambo J, Klatser P (2005) The role and performance of chest X-ray for the diagnosis of tuberculosis: a cost-effectiveness analysis in Nairobi, Kenya. BMC Infect Dis 5: 111 Available: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1326228&tool=p.... Accessed 2012 Nov 7 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Graham S, Das GK, Hidvegi RJ, Hanson R, Kosiuk J, et al. (2002) Chest radiograph abnormalities associated with tuberculosis: reproducibility and yield of active cases. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 6: 137–142 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11931412. Accessed 2012 Oct 2 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

