Household cooking with solid fuels contributes to ambient PM2.5 air pollution and the burden of disease
- PMID: 25192243
- PMCID: PMC4256045
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1206340
Household cooking with solid fuels contributes to ambient PM2.5 air pollution and the burden of disease
Abstract
Background: Approximately 2.8 billion people cook with solid fuels. Research has focused on the health impacts of indoor exposure to fine particulate pollution. Here, for the 2010 Global Burden of Disease project (GBD 2010), we evaluated the impact of household cooking with solid fuels on regional population-weighted ambient PM2.5 (particulate matter ≤ 2.5 μm) pollution (APM2.5).
Objectives: We estimated the proportion and concentrations of APM2.5 attributable to household cooking with solid fuels (PM2.5-cook) for the years 1990, 2005, and 2010 in 170 countries, and associated ill health.
Methods: We used an energy supply-driven emissions model (GAINS; Greenhouse Gas and Air Pollution Interactions and Synergies) and source-receptor model (TM5-FASST) to estimate the proportion of APM2.5 produced by households and the proportion of household PM2.5 emissions from cooking with solid fuels. We estimated health effects using GBD 2010 data on ill health from APM2.5 exposure.
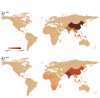
Results: In 2010, household cooking with solid fuels accounted for 12% of APM2.5 globally, varying from 0% of APM2.5 in five higher-income regions to 37% (2.8 μg/m3 of 6.9 μg/m3 total) in southern sub-Saharan Africa. PM2.5-cook constituted > 10% of APM2.5 in seven regions housing 4.4 billion people. South Asia showed the highest regional concentration of APM2.5 from household cooking (8.6 μg/m3). On the basis of GBD 2010, we estimate that exposure to APM2.5 from cooking with solid fuels caused the loss of 370,000 lives and 9.9 million disability-adjusted life years globally in 2010.
Conclusions: PM2.5 emissions from household cooking constitute an important portion of APM2.5 concentrations in many places, including India and China. Efforts to improve ambient air quality will be hindered if household cooking conditions are not addressed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Amann M, Bertok I, Borken-Kleefeld J, Cofala J, Heyes C, Höglund-Isaksson L, et al. Cost-effective control of air quality and greenhouse gases in Europe: modeling and policy applications. Environ Model Softw. 2011;26:1489–1501.
-
- Amann M, Kejun J, Jiming H, Wang S, Xing Z, Wei W, et al. Laxenburg, Austria: International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis; 2008. GAINS Asia Scenarios for Cost-Effective Control of Air Pollution and Greenhouse Gases in China.
-
- Apte JS, Kirchstetter TW, Reich AH, Deshpande SJ, Kaushik G, Chel A, et al. Concentrations of fine, ultrafine, and black carbon particles in auto-rickshaws in new Delhi, India. Atmos Environ. 2011;45:4470–4480.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical