Comprehensive luciferase-based reporter gene assay reveals previously masked up-regulatory effects of miRNAs
- PMID: 25192285
- PMCID: PMC4200788
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms150915592
Comprehensive luciferase-based reporter gene assay reveals previously masked up-regulatory effects of miRNAs
Abstract
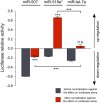
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate the majority of the transcriptome at a post-transcriptional level. Because of this critical role, it is important to ensure that the assays used to determine their functionality are robust and reproducible. Typically, the reporter gene assay in cell-based systems has been the first-line method to study miRNA functionality. In order to overcome some of the potential errors in interpretation that can be associated with this assay, we have developed a detailed protocol for the luciferase reporter gene assay that has been modified for miRNAs. We demonstrate that normalization against the effect of the miRNA and cellular factors on the luciferase coding sequence is essential to obtain the specific impact of the miRNA on the 3'UTR (untranslated region) target. Our findings suggest that there is a real possibility that the roles for miRNA in transcriptome regulation may be misreported due to inaccurate normalization of experimental data and also that up-regulatory effects of miRNAs are not uncommon in cells. We propose to establish this comprehensive method as standard for miRNA luciferase reporter assays to avoid errors and misinterpretations in the functionality of miRNAs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered microRNA expression profile in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a role in the regulation of NFL mRNA levels.Mol Brain. 2013 May 24;6:26. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-6-26. Mol Brain. 2013. PMID: 23705811 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying targets of human micrornas with the LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System using 3'UTR-reporter constructs and a microRNA mimic in adherent cells.J Vis Exp. 2011 Sep 28;(55):3343. doi: 10.3791/3343. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21988797 Free PMC article.
-
Versican 3'-untranslated region (3'UTR) promotes dermal wound repair and fibroblast migration by regulating miRNA activity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jul;1843(7):1373-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.02.015. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24594381
-
A useful method of identifying of miRNAs which can down-regulate Zeb-2.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Nov 18;6:470. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-470. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 24245745 Free PMC article.
-
Small but influential: the role of microRNAs on gene regulatory network and 3'UTR evolution.J Genet Genomics. 2009 Jan;36(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60001-1. J Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19161940 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of Bioinformatic Predictions and Experimental Data to Identify circRNA-miRNA Associations.Genes (Basel). 2019 Aug 24;10(9):642. doi: 10.3390/genes10090642. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31450634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interplay of NEAT1 and miR-339-5p Influences on Mesangial Gene Expression and Function in Various Diabetic-Associated Injury Models.Noncoding RNA. 2022 Jul 13;8(4):52. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8040052. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 35893235 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Profiling in the Prefrontal Cortex: Putative Mechanisms for the Cognitive Effects of Adolescent High Fat Feeding.Sci Rep. 2018 May 29;8(1):8344. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26631-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29844565 Free PMC article.
-
MotomiRs: miRNAs in Motor Neuron Function and Disease.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 May 4;10:127. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00127. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28522960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-9 Promotes Angiogenesis via Targeting on Sphingosine-1- Phosphate Receptor 1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 7;8:755. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00755. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32850858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ma L., Weinberg R.A. Micromanagers of malignancy: Role of microRNAs in regulating metastasis. Trends Genet. 2008;24:448–456. - PubMed
-
- Nilsen T.W. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in animal cells. Trends Genet. 2007;23:243–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

