Multi-drug therapy in chronic condition multimorbidity: a systematic review
- PMID: 25192902
- PMCID: PMC5942538
- DOI: 10.1093/fampra/cmu056
Multi-drug therapy in chronic condition multimorbidity: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Older populations often suffer from multimorbidity and guidelines for each condition are often associated with recommended drug therapy management. Yet, how different and specific multimorbidity is associated with number and type of multi-drug therapies in general populations is unknown.
Aim: The aim of this systematic review was to synthesize the current evidence on patterns of multi-drug prescribing in family practice.
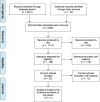
Methods: A systematic review on six common chronic conditions: diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), osteoarthritis and depression was conducted, with a focus on studies which looked at any potential combination of two or more multimorbidity. Studies were identified from searches of MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsychINFO, the Allied and Complementary Medicine Database (AMED) and the Health Management Information Consortium (HMIC) databases from 1960 to 2013.
Results: A total of eleven articles were selected based on study criteria. Our review identified very few specific studies which had explicitly investigated the association between multimorbidity and multi-drug therapy. Relevant chronic conditions literature showed nine observational studies and two reviews of comorbid depression drug treatment. Most (seven) of the articles had focused on the chronic condition and comorbid depression and whether antidepressant management had been optimal or not, while four studies focused on other multimorbidities mainly heart failure, COPD and diabetes.
Conclusions: Very few studies have investigated associations between specific multimorbidity and multi-drug therapy, and most currently focus on chronic disease comorbid depression outcomes. Further research needs to identify this area as key priority for older populations who are prescribed high levels of multiple drug therapy.
Keywords: COPD; Chronic disease; depression; drug therapy; multimorbidity; osteoarthritis..
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- van den Akker M, Buntinx F, Metsemakers JF, Roos S, Knottnerus JA. Multimorbidity in general practice: prevalence, incidence, and determinants of co-occurring chronic and recurrent diseases. J Clin Epidemiol 1998; 51: 367–75. - PubMed
-
- Barnett K, Mercer SW, Norbury M, Watt G, Wyke S, Guthrie B. Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and medical education: a cross-sectional study The Lancet 2012; 6736(12): 60240–2. - PubMed
-
- Wehling M. Multimorbidity and polypharmacy: how to reduce the harmful drug load and yet add needed drugs in the elderly? Proposal of a new drug classification: fit for the aged. J Am Geriatr Soc 2009; 57: 560–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical