Evolution and comparative genomics of Campylobacter jejuni ST-677 clonal complex
- PMID: 25193305
- PMCID: PMC4202330
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evu194
Evolution and comparative genomics of Campylobacter jejuni ST-677 clonal complex
Abstract
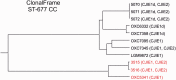
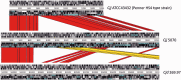
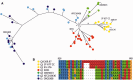
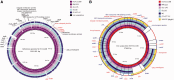
Campylobacter is the most common bacterial cause of gastroenteritis in the European Union with over 200,000 laboratory-confirmed cases reported annually. This is the first study to describe findings related to comparative genomics analyses of the sequence type (ST)-677 clonal complex (CC), a Campylobacter jejuni lineage associated with bacteremia cases in humans. We performed whole-genome sequencing, using Illumina HiSeq sequencing technology, on five related ST-677 CC isolates from two chicken farms to identify microevolution taking place at the farms. Our further aim was to identify novel putative virulence determinants from the ST-677 CC genomes. For this purpose, clinical isolates of the same CC were included in comparative genomic analyses against well-known reference strains of C. jejuni. Overall, the ST-677 CC was recognized as a highly clonal lineage with relatively small differences between the genomes. Among the farm isolates differences were identified mainly in the lengths of the homopolymeric tracts in genes related to the capsule, lipo-oligosaccharide, and flagella. We identified genomic features shared with C. jejuni subsp. doylei, which has also been shown to be associated with bacteremia in humans. These included the degradation of the cytolethal distending toxin operon and similarities between the capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis loci. The phase-variable GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.47) (wcbK, CAMP1649), associated with the capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis locus, may play a central role in ST-677 CC conferring acid and serum resistance during different stages of infection. Homology-based searches revealed several additional novel features and characteristics, including two putative type Vb secretion systems and a novel restriction modification/methyltransferase gene cluster, putatively associated with pathogenesis and niche adaptation.
Keywords: Campylobacter jejuni; bacteremia; capsule; niche adaptation; phase variation; serum resistance.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Population Genetics and Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Western Jackdaws and Game Birds in Finland.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Feb 6;85(4):e02365-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02365-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30552190 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and genome biology of invasive Campylobacter jejuni.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 25;5:17300. doi: 10.1038/srep17300. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26603914 Free PMC article.
-
Accessory genetic content in Campylobacter jejuni ST21CC isolates from feces and blood.Int J Med Microbiol. 2017 Jun;307(4-5):233-240. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Int J Med Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28408091
-
The Current State of Macrolide Resistance in Campylobacter spp.: Trends and Impacts of Resistance Mechanisms.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 May 31;83(12):e00416-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00416-17. Print 2017 Jun 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28411226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Species Delineation and Comparative Genomics within the Campylobacter ureolyticus Complex.J Clin Microbiol. 2023 May 23;61(5):e0004623. doi: 10.1128/jcm.00046-23. Epub 2023 Apr 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37129508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Campylobacter bacteriophage DA10: an excised temperate bacteriophage targeted by CRISPR-cas.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jun 12;21(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06808-3. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32532247 Free PMC article.
-
Local genes for local bacteria: Evidence of allopatry in the genomes of transatlantic Campylobacter populations.Mol Ecol. 2017 Sep;26(17):4497-4508. doi: 10.1111/mec.14176. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Mol Ecol. 2017. PMID: 28493321 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence and Molecular Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni ST-2993 Associated with a Large Outbreak of Guillain-Barré Syndrome in Peru.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0118722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01187-22. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35972275 Free PMC article.
-
Monomorphic genotypes within a generalist lineage of Campylobacter jejuni show signs of global dispersion.Microb Genom. 2016 Oct 21;2(10):e000088. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000088. eCollection 2016 Oct. Microb Genom. 2016. PMID: 28348829 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic Strain-Typing Combined with Isolate Sequencing Provides Increased Resolution of the Genetic Diversity of Campylobacter jejuni Carriage in Wild Birds.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 3;11(1):121. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010121. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36677413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

