Regulatory effects of a Mnk2-eIF4E feedback loop during mTORC1 targeting of human medulloblastoma cells
- PMID: 25193863
- PMCID: PMC4226695
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2319
Regulatory effects of a Mnk2-eIF4E feedback loop during mTORC1 targeting of human medulloblastoma cells
Abstract
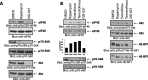
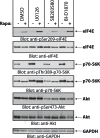
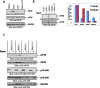
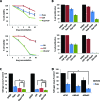
The mTOR pathway controls mRNA translation of mitogenic proteins and is a central regulator of metabolism in malignant cells. Development of malignant cell resistance is a limiting factor to the effects of mTOR inhibitors, but the mechanisms accounting for such resistance are not well understood. We provide evidence that mTORC1 inhibition by rapamycin results in engagement of a negative feedback regulatory loop in malignant medulloblastoma cells, involving phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation-initiation factor eIF4E. This eIF4E phosphorylation is Mnk2- mediated, but Mnk1-independent, and acts as a survival mechanism for medulloblastoma cells. Pharmacological targeting of Mnk1/2 or siRNA-mediated knockdown of Mnk2 sensitizes medulloblastoma cells to mTOR inhibition and promotes suppression of malignant cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth. Altogether, these findings provide evidence for the existence of a Mnk2-controlled feedback loop in medulloblastoma cells that accounts for resistance to mTOR inhibitors, and raise the potential for combination treatments of mTOR and Mnk inhibitors for the treatment of medulloblastoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reciprocal signaling between mTORC1 and MNK2 controls cell growth and oncogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(1):249-270. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03491-1. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32170339 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin induces phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and Mnk-mediated eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;27(21):7405-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00760-07. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17724079 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous inhibition of mTOR-containing complex 1 (mTORC1) and MNK induces apoptosis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024849. Epub 2011 Sep 16. PLoS One. 2011. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2020 Sep 10;15(9):e0239102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239102. PMID: 21949767 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The Enigma of Rapamycin Dosage.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Mar;15(3):347-53. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0720. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26916116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting mTOR globally in cancer: thinking beyond rapamycin.Cell Cycle. 2009 Dec;8(23):3831-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.23.10070. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19901542 Review.
Cited by
-
eIF4E Phosphorylation in Prostate Cancer.Neoplasia. 2018 Jun;20(6):563-573. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 May 4. Neoplasia. 2018. PMID: 29730477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal signaling between mTORC1 and MNK2 controls cell growth and oncogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(1):249-270. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03491-1. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32170339 Free PMC article.
-
HDL nanoparticles targeting sonic hedgehog subtype medulloblastoma.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 19;8(1):1211. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18100-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29352211 Free PMC article.
-
MNK Controls mTORC1:Substrate Association through Regulation of TELO2 Binding with mTORC1.Cell Rep. 2017 Feb 7;18(6):1444-1457. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.023. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28178522 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of Tomivosertib in acute myeloid leukemia.Oncotarget. 2021 May 11;12(10):955-966. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27952. eCollection 2021 May 11. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34012509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pugh TJ, Weeraratne SD, Archer TC, Pomeranz Krummel DA, Auclair D, Bochicchio J, Carneiro MO, Carter SL, Cibulskis K, Erlich RL, Greulich H, Lawrence MS, Lennon NJ, McKenna A, Meldrim J, Ramos AH, et al. Medulloblastoma exome sequencing uncovers subtype-specific somatic mutations. Nature. 2012;488(7409):106–110. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

