Adult lung function and long-term air pollution exposure. ESCAPE: a multicentre cohort study and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25193994
- PMCID: PMC4318659
- DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00130014
Adult lung function and long-term air pollution exposure. ESCAPE: a multicentre cohort study and meta-analysis
Abstract
The chronic impact of ambient air pollutants on lung function in adults is not fully understood. The objective of this study was to investigate the association of long-term exposure to ambient air pollution with lung function in adult participants from five cohorts in the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Residential exposure to nitrogen oxides (NO₂, NOx) and particulate matter (PM) was modelled and traffic indicators were assessed in a standardised manner. The spirometric parameters forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV₁) and forced vital capacity (FVC) from 7613 subjects were considered as outcomes. Cohort-specific results were combined using meta-analysis. We did not observe an association of air pollution with longitudinal change in lung function, but we observed that a 10 μg·m(-3) increase in NO₂ exposure was associated with lower levels of FEV₁ (-14.0 mL, 95% CI -25.8 to -2.1) and FVC (-14.9 mL, 95% CI -28.7 to -1.1). An increase of 10 μg·m(-3) in PM10, but not other PM metrics (PM2.5, coarse fraction of PM, PM absorbance), was associated with a lower level of FEV₁ (-44.6 mL, 95% CI -85.4 to -3.8) and FVC (-59.0 mL, 95% CI -112.3 to -5.6). The associations were particularly strong in obese persons. This study adds to the evidence for an adverse association of ambient air pollution with lung function in adults at very low levels in Europe.
Copyright ©ERS 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Disclosures can be found alongside the online version of this article at
Figures

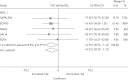
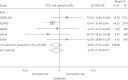
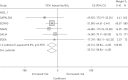
Comment in
-
ESCAPEing from bad-quality air: a cleaner air, from Europe to elsewhere.Eur Respir J. 2015 Jan;45(1):11-3. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00168814. Eur Respir J. 2015. PMID: 25552730 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sunyer J. Lung function effects of chronic exposure to air pollution. Thorax 2009; 64: 645–646. - PubMed
-
- Forbes LJ, Kapetanakis V, Rudnicka AR, et al. . Chronic exposure to outdoor air pollution and lung function in adults. Thorax 2009; 64: 657–663. - PubMed
-
- Ackermann-Liebrich U, Leuenberger P, Schwartz J, et al. . Lung function and long term exposure to air pollutants in Switzerland. Study on Air Pollution and Lung Diseases in Adults (SAPALDIA) Team. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997; 155: 122–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
