Effects of MEK inhibitors GSK1120212 and PD0325901 in vivo using 10-plex quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics
- PMID: 25195567
- PMCID: PMC4515953
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201400154
Effects of MEK inhibitors GSK1120212 and PD0325901 in vivo using 10-plex quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics
Abstract
Multiplexed isobaric tag based quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics strategies can comprehensively analyze drug treatments effects on biological systems. Given the role of mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK) signaling in cancer and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent diseases, we sought to determine if this pathway could be inhibited safely by examining the downstream molecular consequences. We used a series of tandem mass tag 10-plex experiments to analyze the effect of two MEK inhibitors (GSK1120212 and PD0325901) on three tissues (kidney, liver, and pancreas) from nine mice. We quantified ∼ 6000 proteins in each tissue, but significant protein-level alterations were minimal with inhibitor treatment. Of particular interest was kidney tissue, as edema is an adverse effect of these inhibitors. From kidney tissue, we enriched phosphopeptides using titanium dioxide (TiO2 ) and quantified 10 562 phosphorylation events. Further analysis by phosphotyrosine peptide immunoprecipitation quantified an additional 592 phosphorylation events. Phosphorylation motif analysis revealed that the inhibitors decreased phosphorylation levels of proline-x-serine-proline (PxSP) and serine-proline (SP) sites, consistent with extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) inhibition. The MEK inhibitors had the greatest decrease on the phosphorylation of two proteins, Barttin and Slc12a3, which have roles in ion transport and fluid balance. Further studies will provide insight into the effect of these MEK inhibitors with respect to edema and other adverse events in mouse models and human patients.
Keywords: Barttin; Cell biology; GSK1120212; Multiplexing; PD0325901; Phosphoproteomics.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors acknowledge no conflict of interest.
Figures
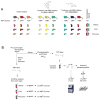

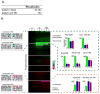
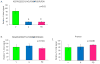
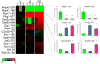
Comment in
-
Proteomics equipped with multiplexing toward ultra high throughput.Proteomics. 2015 Jan;15(2-3):183-4. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400593. Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25522341
References
-
- Dayon L, Hainard A, Licker V, Turck N, et al. Relative quantification of proteins in human cerebrospinal fluids by MS/MS using 6-plex isobaric tags. Anal Chem. 2008;80:2921–2931. - PubMed
-
- Thompson A, Schafer J, Kuhn K, Kienle S, et al. Tandem mass tags: a novel quantification strategy for comparative analysis of complex protein mixtures by MS/MS. Analytical chemistry. 2003;75:1895–1904. - PubMed
-
- Ross PL, Huang YN, Marchese JN, Williamson B, et al. Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP. 2004;3:1154–1169. - PubMed
-
- Wang D, Boerner SA, Winkler JD, LoRusso PM. Clinical experience of MEK inhibitors in cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:1248–1255. - PubMed
-
- Kim KB, Kefford R, Pavlick AC, Infante JR, et al. Phase II study of the MEK1/MEK2 inhibitor Trametinib in patients with metastatic BRAF-mutant cutaneous melanoma previously treated with or without a BRAF inhibitor. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2013;31:482–489. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

