The role of pericyte detachment in vascular rarefaction
- PMID: 25195856
- PMCID: PMC4476411
- DOI: 10.1159/000365149
The role of pericyte detachment in vascular rarefaction
Abstract
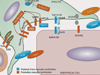
Background: Pericytes surround endothelial cells at the perivascular interface. Signaling between endothelial cells and pericytes is crucial for capillary homeostasis, as pericytes stabilize vessels and regulate many microvascular functions. Recently it has been shown that pericytes are able to detach from the vascular wall and contribute to fibrosis by becoming scar-forming myofibroblasts in many organs including the kidney. At the same time, the loss of pericytes within the perivascular compartment results in vulnerable capillaries which are prone to instability, pathological angiogenesis, and, ultimately, rarefaction.
Aims: This review will give an overview of pericyte-endothelial cell interactions, summarize the signaling pathways that have been identified to be involved in pericyte detachment from the vascular wall, and present pathological endothelial responses in the context of disease of the kidney.
© 2014 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

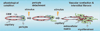
References
-
- Powell DW, Mifflin RC, Valentich JD, Crowe SE, Saada JI, West AB. Myofibroblasts. 1. Paracrine cells important in health and disease. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:C1–C9. - PubMed
-
- Badid C, Desmouliere A, Babici D, Hadj-Aissa A, McGregor B, Lefrancois N, Touraine JL, Laville M. Interstitial expression of alpha-SMA: an early marker of chronic renal allograft dysfunction. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17:1993–1998. - PubMed
-
- Kang DH, Kanellis J, Hugo C, Truong L, Anderson S, Kerjaschki D, Schreiner GF, Johnson RJ. Role of the microvascular endothelium in progressive renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:806–816. - PubMed
-
- Siao CJ, Lorentz CU, Kermani P, Marinic T, Carter J, McGrath K, Padow VA, Mark W, Falcone DJ, Cohen-Gould L, Parrish DC, Habecker BA, Nykjaer A, Ellenson LH, Tessarollo L, Hempstead BL. ProNGF, a cytokine induced after myocardial infarction in humans, targets pericytes to promote microvascular damage and activation. J Exp Med. 2012;209:2291–2305. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

