Effect of simvastatin and atorvastatin on serum vitamin d and bone mineral density in hypercholesterolemic patients: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 25197610
- PMCID: PMC4147265
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/468397
Effect of simvastatin and atorvastatin on serum vitamin d and bone mineral density in hypercholesterolemic patients: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
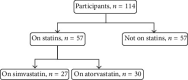
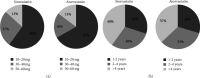
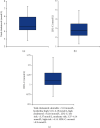
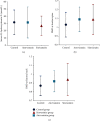
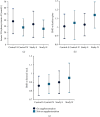
Background. Besides lipid-lowering effect of statins, they have been shown to have nonlipid lowering effects, such as improving bone health. An improvement in bone mineral density (BMD) has been indicated in some studies after the use of statins, in addition to an increase in 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) level. The aim of this study is to explore the association between statins and bone health taking into consideration 25OHD level and BMD. Methods. This is a randomized, cross-sectional comparative study. Subjects were divided into two groups, hypercholesterolemic participants taking simvastatin or atorvastatin as the study group and a matched control group not taking statins. All participants were assessed for serum 25OHD and BMD at lumbar spine and femoral neck. Results. A total of 114 participants were included in the study, 57 participants in each group. Results of serum 25OHD showed no significant difference between study and control groups (P = 0.47), while BMD results of lumbar spine and femoral neck showed significant difference (P = 0.05 and 0.03, resp.). Conclusion. Simvastatin and atorvastatin, at any dose for duration of more than one year, have no additive effect on 25OHD level but have a positive effect on the BMD.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Ardawi is the chairman of the Center of Excellence for Osteoporosis Research, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Dr. Qari is the deputy chairman at the Center of Excellence for Osteoporosis Research, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. All other authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures
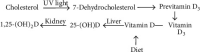
Similar articles
-
Bone mineral density of the spine and femur in healthy Saudi females: relation to vitamin D status, pregnancy, and lactation.Calcif Tissue Int. 1999 Jul;65(1):23-8. doi: 10.1007/s002239900652. Calcif Tissue Int. 1999. PMID: 10369729
-
Effect of simvastatin treatment on bone mineral density and bone turnover in hypercholesterolemic postmenopausal women: a 1-year longitudinal study.Bone. 2003 Apr;32(4):427-33. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(03)00034-6. Bone. 2003. PMID: 12689687
-
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, bone mineral density, and non-vertebral fracture risk in community-dwelling older men: results from Mr. Os, Hong Kong.Arch Osteoporos. 2011;6:21-30. doi: 10.1007/s11657-011-0053-0. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Arch Osteoporos. 2011. PMID: 22886099
-
Effect of increasing doses of vitamin D on bone mineral density and serum N-terminal telopeptide in elderly women: a randomized controlled trial.J Intern Med. 2018 Dec;284(6):685-693. doi: 10.1111/joim.12825. Epub 2018 Sep 17. J Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 30137647
-
Serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and its association with bone mineral density and serum parathyroid hormone levels during winter in urban males from Guiyang, Southwest China.Br J Nutr. 2016 Mar 28;115(6):960-6. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515005383. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26843386
Cited by
-
Early Effects of Atorvastatin on Vitamin D and Parathyroid Hormone Serum Levels Following Acute Myocardial Infarction.J Res Pharm Pract. 2019 Jan-Mar;8(1):7-12. doi: 10.4103/jrpp.JRPP_18_55. J Res Pharm Pract. 2019. PMID: 30911557 Free PMC article.
-
Discontinuation of simvastatin leads to a rebound phenomenon and results in immediate peri-implant bone loss.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2016 Mar 18;2(1):65-72. doi: 10.1002/cre2.23. eCollection 2016 Jun. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2016. PMID: 29744151 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of statins, metformin, spironolactone and combined oral contraceptives in reducing testosterone levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.BMC Womens Health. 2020 Apr 5;20(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12905-020-00919-5. BMC Womens Health. 2020. PMID: 32248801 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D3 deficiency and osteopenia in spastic paraplegia type 5 indicate impaired bone homeostasis.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;14(1):7335. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53057-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38538623 Free PMC article.
-
To study impact of treatment with Rosuvastatin versus Atorvastatin on 25 hydroxy Vitamin D concentrations among adult Indian men- a randomized control trial.Indian J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep-Oct;52(5):365-371. doi: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_93_18. Indian J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33283767 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Brunton L., Lazo J., Parker K. Goodman & Gilman's the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 13th. New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill; 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

