Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of selected natural compounds contained in a dietary supplement on two human immortalized keratinocyte lines
- PMID: 25197638
- PMCID: PMC4150458
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/327452
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of selected natural compounds contained in a dietary supplement on two human immortalized keratinocyte lines
Abstract
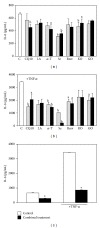
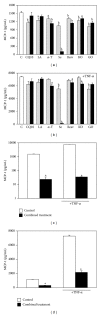
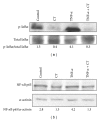
Several advantages may derive from the use of dietary supplements containing multiple natural antioxidants and/or anti-inflammatory agents. At present, however, there is scarce information on the properties and potential of combined supplements. To fill the gap, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities exerted by a combination of seven natural components (coenzyme Q10, krill oil, lipoic acid, resveratrol, grape seed oil, α-tocopherol, and selenium) contained in a dietary supplement used for the prevention of skin disorders were investigated in vitro. Each component was administered, alone or in combination, to human keratinocytes, and the inhibition of Reactive Oxygen Species production and lipid peroxidation as well as the ability to reduce inflammatory cytokine secretion and to modulate Nuclear Factor-κB pathway was evaluated. The combination exhibited high antioxidant activity and in specific conditions the combination's efficiency was higher than that of the most powerful components administered individually. Moreover, the combination showed remarkable anti-inflammatory properties. It reduced more efficiently than each component the secretion of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1, a crucial cytokine for the development of chronic inflammation in skin, and inhibited Nuclear Factor-κB molecular pathway. Overall, our findings suggest that the combined formulation may have the potential to powerfully inhibit oxidative stress and inflammation at skin level.
Figures






References
-
- Calviello G, Su H, Weylandt KH, Fasano E, Serini S, Cittadini A. Experimental evidence of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid modulation of inflammatory cytokines and bioactive lipid mediators: their potential role in inflammatory, neurodegenerative, and neoplastic diseases. BioMed Research International. 2013;2013:13 pages.743171 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manfredini S, Vertuani S, Manfredi B, Rossoni G, Calviello G, Palozza P. Novel antioxidant agents deriving from molecular combinations of vitamins C and E analogues: 3,4-dihydroxy-5(R) Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry. 2000;8(12):2791–2801. - PubMed
-
- Trombino S, Serini S, di Nicuolo F, et al. Antioxidant effect of ferulic acid in isolated membranes and intact cells: synergistic interactions with alpha-tocopherol, beta-carotene, and ascorbic acid. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2004;52(8):2411–2420. - PubMed
-
- Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud C. Antioxidant supplements and mortality. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care. 2014;17(1):40–44. - PubMed
-
- Speciale A, Chirafisi J, Saija A, Cimino F. Nutritional antioxidants and adaptive cell responses: an update. Current Molecular Medicine. 2011;11(9):770–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

