Early glottic cancer: role of MRI in the preoperative staging
- PMID: 25197667
- PMCID: PMC4150401
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/890385
Early glottic cancer: role of MRI in the preoperative staging
Abstract
Introduction: Clinical staging is the most important time in management of glottic cancer in early stage (I-II). We have conducted a prospective study to evaluate if magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more accurate than computed tomography (CT) about tumoral extension, to exactly choose the most appropriate surgical approach, from organ preservation surgery to demolitive surgery. MATERIALS and
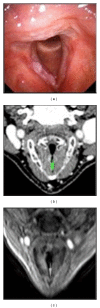
Methods: This prospective study was conducted on 26 male patients, with suspected laryngeal neoplasia of glottic region. The images of MRI and CT were analyzed to define the expansion of glottic lesion to anterior commissure, laryngeal cartilages, subglottic and/or supraglottic site, and paraglottic space. The results of MRI and CT were compared with each other and with the pathology report.
Results: CT accuracy was 70% with low sensitivity but with high specific value. MRI showed a diagnostic accuracy in 80% of cases, with a sensitivity of 100% and high specificity. Statistical analysis showed that MRI has higher correlation than CT with the pathology report.
Conclusion: Our study showed that MRI is more sensitive than CT in the preoperative staging of early glottic cancer, to select exactly the eligible patients in conservative surgery of the larynx, as supracricoid laryngectomy and cordectomy by CO2 laser.
Figures

References
-
- Ortholan C, Benezery K, Dassonville O, et al. A specific approach for elderly patients with head and neck cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22(27):647–655. - PubMed
-
- Hartl DM, Ferlito A, Brasnu DM, et al. Evidence-based review of treatment options for patients with glottic cancer. Head & Neck. 2011;33(11):1638–1648. - PubMed
-
- Chone CT, Yonehara E, Martins JEF, Altemani A, Crespo AN. Importance of anterior commissure in recurrence of early glottic cancer after laser endoscopic resection. Archives of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. 2007;133(9):882–887. - PubMed
-
- Garozzo A, Allegra E, La Boria A, Lombardo N. Modified supracricoid laryngectomy. Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. 2010;142(1):137–139. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

