Feasibility of frequency-modulated wireless transmission for a multi-purpose MEMS-based accelerometer
- PMID: 25198003
- PMCID: PMC4208187
- DOI: 10.3390/s140916563
Feasibility of frequency-modulated wireless transmission for a multi-purpose MEMS-based accelerometer
Abstract
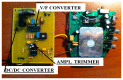
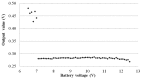
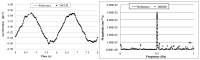
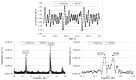
Recent advances in the Micro Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) technology have made wireless MEMS accelerometers an attractive tool for Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) of civil engineering structures. To date, sensors' low sensitivity and accuracy--especially at very low frequencies--have imposed serious limitations for their application in monitoring large-sized structures. Conventionally, the MEMS sensor's analog signals are converted to digital signals before radio-frequency (RF) wireless transmission. The conversion can cause a low sensitivity to the important low-frequency and low-amplitude signals. To overcome this difficulty, the authors have developed a MEMS accelerometer system, which converts the sensor output voltage to a frequency-modulated signal before RF transmission. This is achieved by using a Voltage to Frequency Conversion (V/F) instead of the conventional Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC). In this paper, a prototype MEMS accelerometer system is presented, which consists of a transmitter and receiver circuit boards. The former is equipped with a MEMS accelerometer, a V/F converter and a wireless RF transmitter, while the latter contains an RF receiver and a F/V converter for demodulating the signal. The efficacy of the MEMS accelerometer system in measuring low-frequency and low-amplitude dynamic responses is demonstrated through extensive laboratory tests and experiments on a flow-loop pipeline.
Figures
























References
-
- Sohn H., Farrar C.R., Francois M.H., Jerry J.C., Devin D.S., Daniel W.S., Brett R.N. A Review of Structural Health Monitoring Literature: 1996–2001. [(accessed on 18 July 2014)]. Los Alamos National Laboratory Report, LA-13976-Ms, Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2004. Available online: http://institute.lanl.gov/ei/shm/pubs/LA_13976_MSa.pdf.
-
- Park G., Sohn H., Farrar C.R., Inman D.J. Overview of piezoelectric impedance-based health monitoring and path forward. Shock Vib. Dig. 2003;35:451–463.
-
- Bhalla S., Soh C.K. Structural health monitoring by piezo-impedance transducers. II: Applications. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2004;17:166–175.
-
- Park S., Lee J.J., Yun C.B., Inman D.J. Electro-Mechanical impedance-based wireless structural health monitoring using PCA-data compression and k-means clustering algorithms. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2008;19:509–520.
-
- Annamdas V.G.M., Radhika M.A. Electromechanical impedance of piezoelectric transducers for monitoring metallic and non-metallic structures: A review of wired, wireless and energy-harvesting methods. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2013;24:1021–1042.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

