Intrinsic differences between oral and skin keratinocytes
- PMID: 25198578
- PMCID: PMC4157746
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101480
Intrinsic differences between oral and skin keratinocytes
Abstract
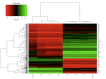
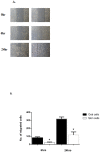
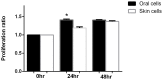
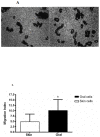
Keratinocytes cover both the skin and some oral mucosa, but the morphology of each tissue and the behavior of the keratinocytes from these two sites are different. One significant dissimilarity between the two sites is the response to injury. Oral mucosal wounds heal faster and with less inflammation than equivalent cutaneous wounds. We hypothesized that oral and skin keratinocytes might have intrinsic differences at baseline as well as in the response to injury, and that such differences would be reflected in gene expression profiles.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Asikainen TM, Ahmad A, Schneider BK, Ho WB, Arend M, et al. (2005) Stimulation of HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, and VEGF by prolyl 4-hydroxylase inhibition in human lung endothelial and epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 38: 1002–1013.. - PubMed
-
- Angelov N, Moutsopoulos N, Jeong M, Nares S, Ashcroft G, et al. (2004) Aberrant mucosal wound repair in the absence of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor. Thromb Haemost 92: 288–97. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft GS, Lei K, Jin W, Longenecker G, Kulkarni AB, et al. (2000) Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor mediates non-redundant functions necessary for normal wound healing. Nat Med 61: 1147–53. - PubMed
-
- Bussi M, De Stefani A, Milan F, Lerda W, Ferrero V, et al. (1995) Is transposed skin transformed in major head and neck mucosal reconstruction? Acta Oto-Laryngologica. 115: 348–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

