Treatment for LTBI in contacts of MDR-TB patients, Federated States of Micronesia, 2009-2012
- PMID: 25199004
- PMCID: PMC4730114
- DOI: 10.5588/ijtld.13.0028
Treatment for LTBI in contacts of MDR-TB patients, Federated States of Micronesia, 2009-2012
Abstract
Setting: Few studies have shown the operational feasibility, safety, tolerability, or outcomes of multidrug-resistant latent tuberculous infection (MDR LTBI) treatment. After two simultaneous multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) outbreaks in Chuuk, Federated States of Micronesia, infected contacts were offered a 12-month fluoroquinolone (FQ) based MDR LTBI treatment regimen.
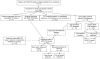
Design: Between January 2009 and February 2012, 119 contacts of MDR-TB patients were followed using a prospective observational study design. After MDR-TB disease was excluded, 12 months of daily FQ-based preventive treatment of MDR LTBI was provided by directly observed therapy.
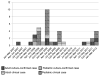
Results: Among the 119 infected contacts, 15 refused, while 104 began treatment for MDR LTBI. Of the 104 who initiated treatment, 93 (89%) completed treatment, while 4 contacts discontinued due to adverse effects. None of the 104 contacts who undertook MDR LTBI treatment of any duration developed MDR-TB disease; however, 3 of 15 contacts who refused and 15 unidentified contacts developed MDR-TB disease.
Conclusion: Providing treatment for MDR LTBI can be accomplished in a resource-limited setting, and contributed to preventing MDR-TB disease. The Chuuk TB program implemented treatment of MDR LTBI with an 89% completion rate. The MDR LTBI regimens were safe and well tolerated, and no TB cases occurred among persons treated for MDR LTBI.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
A new paradigm for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis?Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2014 Aug;18(8):884. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.14.0347. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2014. PMID: 25198999 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report, 2013. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2013. WHO/HTM/TB/2013.11.
-
- Orenstein EW, Basu S, Shah S, et al. Treatment outcomes among patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9:153–161. - PubMed
-
- van Soolingen D, Borgdorff MW, de Haas PE, et al. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in the Netherlands: a nationwide study from 1993 through 1997. JInfect Dis. 1999;180:726–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

