Transcriptional complexity and roles of Fra-1/AP-1 at the uPA/Plau locus in aggressive breast cancer
- PMID: 25200076
- PMCID: PMC4176185
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku814
Transcriptional complexity and roles of Fra-1/AP-1 at the uPA/Plau locus in aggressive breast cancer
Abstract
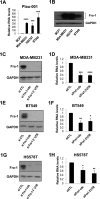
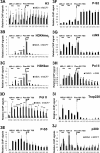
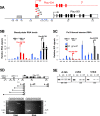
Plau codes for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), critical in cancer metastasis. While the mechanisms driving its overexpression in tumorigenic processes are unknown, it is regulated by the AP-1 transcriptional complex in diverse situations. The AP-1 component Fra-1 being overexpressed in aggressive breast cancers, we have addressed its role in the overexpression of Plau in the highly metastatic breast cancer model cell line MDA-MB231 using ChIP, pharmacological and RNAi approaches. Plau transcription appears controlled by 2 AP-1 enhancers located -1.9 (ABR-1.9) and -4.1 kb (ABR-4.1) upstream of the transcription start site (TSS) of the uPA-coding mRNA, Plau-001, that bind Fra-1. Surprisingly, RNA Pol II is not recruited only at the Plau-001 TSS but also upstream in the ABR-1.9 and ABR-4.1 region. Most Pol II molecules transcribe short and unstable RNAs while tracking down toward the TSS, where there are converted into Plau-001 mRNA-productive species. Moreover, a minority of Pol II molecules transcribes a low abundance mRNA of unknown function called Plau-004 from the ABR-1.9 domain, whose expression is tempered by Fra-1. Thus, we unveil a heretofore-unsuspected transcriptional complexity at Plau in a reference metastatic breast cancer cell line with pleiotropic effects for Fra-1, providing novel information on AP-1 transcriptional action.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- Blasi F., Sidenius N. The urokinase receptor: focused cell surface proteolysis, cell adhesion and signaling. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:1923–1930. - PubMed
-
- Lamy P.-J., Romieu G., Jacot W. [UPA/PAI-1: a tool for breast cancer treatment individualization. Biology, clinical implications and quantification assays] Bull. Cancer (Paris) 2010;97:341–348. - PubMed
-
- Smith H.W., Marshall C.J. Regulation of cell signalling by uPAR. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010;11:23–36. - PubMed
-
- Harbeck N., Schmitt M., Meisner C., Friedel C., Untch M., Schmidt M., Sweep C.G.J., Lisboa B.W., Lux M.P., Beck T., et al. Ten-year analysis of the prospective multicentre Chemo-N0 trial validates American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO)-recommended biomarkers uPA and PAI-1 for therapy decision making in node-negative breast cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990. 2013;49:1825–1835. - PubMed
-
- Cirillo G., Casalino L., Vallone D., Caracciolo A., De Cesare D., Verde P. Role of distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and cooperation between Ets-2, ATF-2, and Jun family members in human urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene induction by interleukin-1 and tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999;19:6240–6252. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

