Distinct tmRNA sequence elements facilitate RNase R engagement on rescued ribosomes for selective nonstop mRNA decay
- PMID: 25200086
- PMCID: PMC4176180
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku802
Distinct tmRNA sequence elements facilitate RNase R engagement on rescued ribosomes for selective nonstop mRNA decay
Abstract
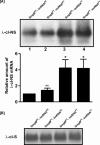
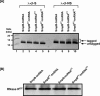
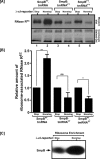
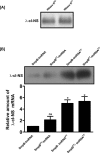
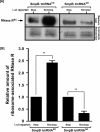
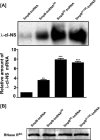
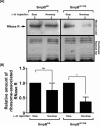
trans-Translation, orchestrated by SmpB and tmRNA, is the principal eubacterial pathway for resolving stalled translation complexes. RNase R, the leading nonstop mRNA surveillance factor, is recruited to stalled ribosomes in a trans-translation dependent process. To elucidate the contributions of SmpB and tmRNA to RNase R recruitment, we evaluated Escherichia coli-Francisella tularensis chimeric variants of tmRNA and SmpB. This evaluation showed that while the hybrid tmRNA supported nascent polypeptide tagging and ribosome rescue, it suffered defects in facilitating RNase R recruitment to stalled ribosomes. To gain further insights, we used established tmRNA and SmpB variants that impact distinct stages of the trans-translation process. Analysis of select tmRNA variants revealed that the sequence composition and positioning of the ultimate and penultimate codons of the tmRNA ORF play a crucial role in recruiting RNase R to rescued ribosomes. Evaluation of defined SmpB C-terminal tail variants highlighted the importance of establishing the tmRNA reading frame, and provided valuable clues into the timing of RNase R recruitment to rescued ribosomes. Taken together, these studies demonstrate that productive RNase R-ribosomes engagement requires active trans-translation, and suggest that RNase R captures the emerging nonstop mRNA at an early stage after establishment of the tmRNA ORF as the surrogate mRNA template.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Active and accurate trans-translation requires distinct determinants in the C-terminal tail of SmpB protein and the mRNA-like domain of transfer messenger RNA (tmRNA).J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 18;288(42):30527-30542. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.503896. Epub 2013 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23986442 Free PMC article.
-
Studying tmRNA-mediated surveillance and nonstop mRNA decay.Methods Enzymol. 2008;447:329-58. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)02217-9. Methods Enzymol. 2008. PMID: 19161851
-
RNase R degrades non-stop mRNAs selectively in an SmpB-tmRNA-dependent manner.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Dec;62(6):1700-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05472.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17087776
-
The tmRNA system for translational surveillance and ribosome rescue.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:101-24. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142733. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17291191 Review.
-
A salvage pathway for protein structures: tmRNA and trans-translation.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:101-23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090945. Epub 2003 May 1. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12730326 Review.
Cited by
-
Ribosome Rescue Pathways in Bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 18;12:652980. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.652980. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33815344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosomal frameshifting and transcriptional slippage: From genetic steganography and cryptography to adventitious use.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7007-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw530. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27436286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into RNA unwinding and degradation by RNase R.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 16;45(20):12015-12024. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx880. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29036353 Free PMC article.
-
Carrot and stick: how RNase R contributes to function and destruction of the translation machinery.RNA Biol. 2025 Dec;22(1):1-22. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2535846. Epub 2025 Jul 29. RNA Biol. 2025. PMID: 40734258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision Genome Engineering in Streptococcus suis Based on a Broad-Host-Range Vector and CRISPR-Cas9 Technology.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Sep 15;12(9):2546-2560. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00110. Epub 2023 Aug 21. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 37602730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karzai A.W., Roche E.D., Sauer R.T. The SsrA-SmpB system for protein tagging, directed degradation and ribosome rescue. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000;7:449–455. - PubMed
-
- Withey J.H., Friedman D.I. A salvage pathway for protein structures: tmRNA and trans-translation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003;57:101–123. - PubMed
-
- Dulebohn D., Choy J., Sundermeier T., Okan N., Karzai A.W. Trans-translation: the tmRNA-mediated surveillance mechanism for ribosome rescue, directed protein degradation, and nonstop mRNA decay. Biochemistry. 2007;46:4681–4693. - PubMed
-
- Barends S., Kraal B., van Wezel G.P. The tmRNA-tagging mechanism and the control of gene expression: a review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2011;2:233–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

