Effects of gastric bypass surgery in patients with hypertension: rationale and design for a randomised controlled trial (GATEWAY study)
- PMID: 25200559
- PMCID: PMC4158200
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005702
Effects of gastric bypass surgery in patients with hypertension: rationale and design for a randomised controlled trial (GATEWAY study)
Abstract
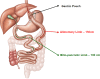
Introduction: Obesity and overweight are becoming progressively more prevalent worldwide and are independently associated with a significant increase in the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Systemic arterial hypertension is frequently found in association with obesity and contributes significantly to increased cardiovascular risk. We hypothesise that Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery, a procedure that effectively reduces body weight, can also positively impact blood pressure control in obese and hypertensive individuals.
Methods and analysis: A unicentric, randomised, controlled, unblinded clinical trial. Sixty obese (body mass index between 30 and 39.9) and moderately well controlled hypertensive patients, in use of at least two antihypertensive medications at maximum doses or more than two in moderate doses, will be randomly allocated, using an online, electronic and concealed method, to receive either RYGB plus optimised clinical treatment (OCT) or OCT alone. The primary end point is the reduction of antihypertensive medication at 1 and 2 years of follow-up. Data analysis will primarily be conducted on an intention-to-treat basis.
Ethics and dissemination: The study was approved by the local institutional review board that works in total compliance with the latest version of the Helsinki Declaration, the Good Clinical Practices (GCP), the 'America's Document' and the national regulatory laws. Before the beginning of any study-related activities, each study participant is asked to provide a signed informed consent.
Trial registration number: NCT01784848.
Keywords: NUTRITION & DIETETICS.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
References
-
- [No authors listed] Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 2000;894:i–xii, 1–253 - PubMed
-
- Mendis S, Lindholm LH, Mancia G, et al. World Health Organization (WHO) and International Society of Hypertension (ISH) risk prediction charts: assessment of cardiovascular risk for prevention and control of cardiovascular disease in low and middle-income countries. J Hypertens 2007;25:1578–82 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials