Maresin-like lipid mediators are produced by leukocytes and platelets and rescue reparative function of diabetes-impaired macrophages
- PMID: 25200603
- PMCID: PMC4224612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.06.010
Maresin-like lipid mediators are produced by leukocytes and platelets and rescue reparative function of diabetes-impaired macrophages
Abstract
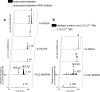
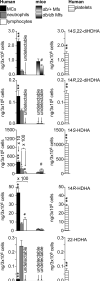
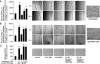
Nonhealing diabetic wounds are associated with impaired macrophage (Mf) function. Leukocytes and platelets (PLT) play crucial roles in wound healing by poorly understood mechanisms. Here we report the identification and characterization of the maresin-like(L) mediators 14,22-dihydroxy-docosa-4Z,7Z,10Z,12E,16Z,19Z-hexaenoic acids, 14S,22-diHDHA (maresin-L1), and 14R,22-diHDHA (maresin-L2) that are produced by leukocytes and PLT and involved in wound healing. We show that 12-lipoxygenase-initiated 14S-hydroxylation or cytochrome P450 catalyzed 14R-hydroxylation and P450-initiated ω(22)-hydroxylation are required for maresin-L biosynthesis. Maresin-L treatment restores reparative functions of diabetic Mfs, suggesting that maresin-Ls act as autocrine/paracrine factors responsible for, at least in part, the reparative functions of leukocytes and PLT in wounds. Additionally, maresin-L ameliorates Mf inflammatory activation and has the potential to suppress the chronic inflammation in diabetic wounds caused by activation of Mfs. These findings provide initial insights into maresin-L biosynthesis and mechanism of action and potentially offer a therapeutic option for better treatment of diabetic wounds.
Figures
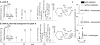



References
-
- Biswas SK, Mantovani A. Orchestration of metabolism by macrophages. Cell metabolism. 2012;15:432–437. - PubMed
-
- Capdevila JH, Holla VR, Faick JR. Cytochrome P450 and the Metabolism and Bioactivation of Arachidonic Acid and Eicosanoids. In: Paul R.O.d.M., editor. Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry, 3e. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; New York: 2005.
-
- Chiang N, Takano T, Clish CB, Petasis NA, Tai HH, Serhan CN. Aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin A4 (ATL) generation by human leukocytes and murine peritonitis exudates: development of a specific 15-epi-LXA4 ELISA. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 1998;287:779–790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

