QRS-T angle: a review
- PMID: 25201032
- PMCID: PMC4237708
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.12206
QRS-T angle: a review
Abstract
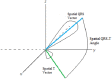
For proper distribution of preventative resources, a more robust method of cardiac risk stratification should be encouraged in addition to merely reduced ejection fraction. To this end, the QRS-T angle, an electrocardiogram-derived measure of the difference in mean vectors of depolarization and repolarization, has been found associated with sudden cardiac death and other mortal and morbid outcomes in multiple observational studies over the past decade. The use of both frontal and spatial QRS-T angle in the prediction of future cardiac events including sudden cardiac death, all-cause mortality, and further cardiac morbidity is reviewed here.
Keywords: cardiac arrest; clinical; electrocardiography; electrophysiology; noninvasive techniques; sudden death.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Mann H. A method of analyzing the electrocardiogram. Arch Intern Med 1920;25:283–94.
-
- Einthoven W. Over de beteekenis der electro‐physiologie als een onderdeel van de leer der levensverrichtingen. Leiden Brill 1906, pp 1–34.
-
- Frank E. An accurate, clinically practical system for spatial vectorcardiography. Circulation 1956;13:737–749. - PubMed
-
- Wilson FN, Macleod AG, Barker PS, et al. The determination and the significance of the areas of the ventricular deflections of the electrocardiogram. Am Heart J 1934;10:46–61.
-
- Geselowitz DB. The ventricular gradient revisited: relation to the area under the action potential. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1983;30:76–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous