Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer
- PMID: 25201530
- PMCID: PMC4237931
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.016
Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer
Abstract
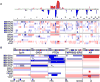
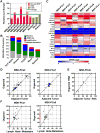
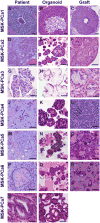
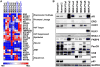
The lack of in vitro prostate cancer models that recapitulate the diversity of human prostate cancer has hampered progress in understanding disease pathogenesis and therapy response. Using a 3D organoid system, we report success in long-term culture of prostate cancer from biopsy specimens and circulating tumor cells. The first seven fully characterized organoid lines recapitulate the molecular diversity of prostate cancer subtypes, including TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, SPOP mutation, SPINK1 overexpression, and CHD1 loss. Whole-exome sequencing shows a low mutational burden, consistent with genomics studies, but with mutations in FOXA1 and PIK3R1, as well as in DNA repair and chromatin modifier pathways that have been reported in advanced disease. Loss of p53 and RB tumor suppressor pathway function are the most common feature shared across the organoid lines. The methodology described here should enable the generation of a large repertoire of patient-derived prostate cancer lines amenable to genetic and pharmacologic studies.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
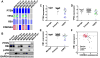
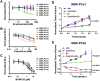
Comment in
-
Innovation: organoids-a better model for prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2014 Nov;11(11):604. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2014.269. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Nat Rev Urol. 2014. PMID: 25245237 No abstract available.
-
Cell biology: Prostate cancer in 3D.Nat Methods. 2014 Nov;11(11):1096. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3167. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 25551127 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barker N, Huch M, Kujala P, van de Wetering M, Snippert HJ, van Es JH, Sato T, Stange DE, Begthel H, van den Born M, et al. Lgr5(+ve) stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell stem cell. 2010;6:25–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P50CA092629/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA155169-01A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA092629/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155169/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA116337/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116337/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA182503/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA193837/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5K08CA140946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA140946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000457/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA151660/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

