Developmental relations between vocabulary knowledge and reading comprehension: a latent change score modeling study
- PMID: 25201552
- PMCID: PMC4331220
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.12292
Developmental relations between vocabulary knowledge and reading comprehension: a latent change score modeling study
Abstract
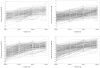
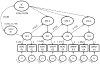
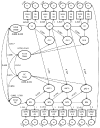
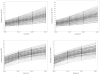
The present study followed a sample of first-grade (N = 316, Mage = 7.05 at first test) through fourth-grade students to evaluate dynamic developmental relations between vocabulary knowledge and reading comprehension. Using latent change score modeling, competing models were fit to the repeated measurements of vocabulary knowledge and reading comprehension to test for the presence of leading and lagging influences. Univariate models indicated growth in vocabulary knowledge, and reading comprehension was determined by two parts: constant yearly change and change proportional to the previous level of the variable. Bivariate models indicated previous levels of vocabulary knowledge acted as leading indicators of reading comprehension growth, but the reverse relation was not found. Implications for theories of developmental relations between vocabulary and reading comprehension are discussed.
© 2014 The Authors. Child Development © 2014 Society for Research in Child Development, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Abelson RP. A variance explanation paradox: When a little is a lot. Psychological Bulletin. 1985;97:129–133. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.97.1.129. - DOI
-
- Anderson R, Freebody P. Vocabulary knowledge. In: Guthrie JT, editor. Comprehension and teaching: Research reviews. Newark, DE: International Reading Association; 1981. pp. 77–117.
-
- Beck I, McKeown M. Conditions of vocabulary acquisition. In: Barr R, Kamil ML, Mosenthal PB, Pearson PD, editors. Handbook of reading research. New York: Longman; 1991. pp. 789–814.
-
- Beck I, Perfetti C, McKeown M. Effects of long-term vocabulary instruction on lexical access and reading comprehension. Journal of Educational Psychology. 1982;74:506–521. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.74.4.506. - DOI
-
- Cain K. Deriving word meanings from context: Does explanation facilitate contextual analysis? Journal of Research in Reading. 2007;30:347–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9817.2007.00336.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

