Heterodimeric capping protein from Arabidopsis is a membrane-associated, actin-binding protein
- PMID: 25201878
- PMCID: PMC4226361
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.242487
Heterodimeric capping protein from Arabidopsis is a membrane-associated, actin-binding protein
Abstract
The actin cytoskeleton is a major regulator of cell morphogenesis and responses to biotic and abiotic stimuli. The organization and activities of the cytoskeleton are choreographed by hundreds of accessory proteins. Many actin-binding proteins are thought to be stimulus-response regulators that bind to signaling phospholipids and change their activity upon lipid binding. Whether these proteins associate with and/or are regulated by signaling lipids in plant cells remains poorly understood. Heterodimeric capping protein (CP) is a conserved and ubiquitous regulator of actin dynamics. It binds to the barbed end of filaments with high affinity and modulates filament assembly and disassembly reactions in vitro. Direct interaction of CP with phospholipids, including phosphatidic acid, results in uncapping of filament ends in vitro. Live-cell imaging and reverse-genetic analyses of cp mutants in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) recently provided compelling support for a model in which CP activity is negatively regulated by phosphatidic acid in vivo. Here, we used complementary biochemical, subcellular fractionation, and immunofluorescence microscopy approaches to elucidate CP-membrane association. We found that CP is moderately abundant in Arabidopsis tissues and present in a microsomal membrane fraction. Sucrose density gradient separation and immunoblotting with known compartment markers were used to demonstrate that CP is enriched on membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. This association could facilitate cross talk between the actin cytoskeleton and a wide spectrum of essential cellular functions such as organelle motility and signal transduction.
© 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
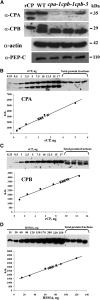

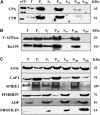



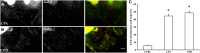
References
-
- Baillie GS, Huston E, Scotland G, Hodgkin M, Gall I, Peden AH, MacKenzie C, Houslay ES, Currie R, Pettitt TR, et al. (2002) TAPAS-1, a novel microdomain within the unique N-terminal region of the PDE4A1 cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase that allows rapid, Ca2+-triggered membrane association with selectivity for interaction with phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem 277: 28298–28309 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

