Osmotic stress-induced phosphorylation of H2AX by polo-like kinase 3 affects cell cycle progression in human corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 25202016
- PMCID: PMC4207995
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.597161
Osmotic stress-induced phosphorylation of H2AX by polo-like kinase 3 affects cell cycle progression in human corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
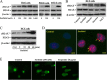
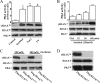
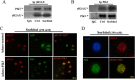
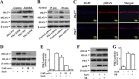
Increased concentrations of extracellular solutes affect cell function and fate by stimulating cellular responses, such as evoking MAPK cascades, altering cell cycle progression, and causing apoptosis. Our study results here demonstrate that hyperosmotic stress induced H2AX phosphorylation (γH2AX) by an unrevealed kinase cascade involving polo-like kinase 3 (Plk3) in human corneal epithelial (HCE) cells. We found that hyperosmotic stress induced DNA-double strand breaks and increased γH2AX in HCE cells. Phosphorylation of H2AX at serine 139 was catalyzed by hyperosmotic stress-induced activation of Plk3. Plk3 directly interacted with H2AX and was colocalized with γH2AX in the nuclei of hyperosmotic stress-induced cells. Suppression of Plk3 activity by overexpression of a kinase-silencing mutant or by knocking down Plk3 mRNA effectively reduced γH2AX in hyperosmotic stress-induced cells. This was consistent with results that show γH2AX was markedly suppressed in the Plk3(-/-) knock-out mouse corneal epithelial layer in response to hyperosmotic stimulation. The effect of hyperosmotic stress-activated Plk3 and increased γH2AX in cell cycle progression showed an accumulation of G2/M phase, altered population in G1 and S phases, and increased apoptosis. Our results for the first time reveal that hyperosmotic stress-activated Plk3 elicited γH2AX. This Plk3-mediated activation of γH2AX subsequently regulates the cell cycle progression and cell fate.
Keywords: Cell Cycle; Cornea; Epithelial Cell; H2A Histone Family, Member X (H2AFX); Phosphorylation; Signaling.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Foulks G. N. (2007) The correlation between the tear film lipid layer and dry eye disease. Surv. Ophthalmol. 52, 369–374 - PubMed
-
- Wu S. G., Jeng F. R., Wei S. Y., Su C. Z., Chung T. C., Chang W. J., Chang H. W. (1998) Red blood cell osmotic fragility in chronically hemodialyzed patients. Nephron. 78, 28–32 - PubMed
-
- Mitono H., Endoh H., Okazaki K., Ichinose T., Masuki S., Takamata A., Nose H. (2005) Acute hypoosmolality attenuates the suppression of cutaneous vasodilation with increased exercise intensity. J. Appl. Physiol. 99, 902–908 - PubMed
-
- Ito T., Itoh T., Hayano T., Yamauchi K., Takamata A. (2005) Plasma hyperosmolality augments peripheral vascular response to baroreceptor unloading during heat stress. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 289, R432–R440 - PubMed
-
- Burg M. B., Ferraris J. D., Dmitrieva N. I. (2007) Cellular response to hyperosmotic stresses. Physiol. Rev. 87, 1441–1474 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

