C-type lectin receptor dectin-3 mediates trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM)-induced Mincle expression through CARD9/Bcl10/MALT1-dependent nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation
- PMID: 25202022
- PMCID: PMC4208012
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.588574
C-type lectin receptor dectin-3 mediates trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM)-induced Mincle expression through CARD9/Bcl10/MALT1-dependent nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation
Abstract
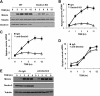
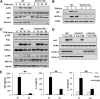
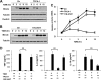
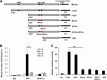
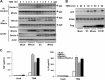
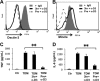
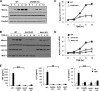
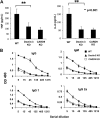
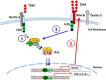
Previous studies indicate that both Dectin-3 (also called MCL or Clec4d) and Mincle (also called Clec4e), two C-type lectin receptors, can recognize trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM), a cell wall component from mycobacteria, and induce potent innate immune responses. Interestingly, stimulation of Dectin-3 by TDM can also induce Mincle expression, which may enhance the host innate immune system to sense Mycobacterium infection. However, the mechanism by which Dectin-3 induces Mincle expression is not fully defined. Here, we show that TDM-induced Mincle expression is dependent on Dectin-3-mediated NF-κB, but not nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT), activation, and Dectin-3 induces NF-κB activation through the CARD9-BCL10-MALT1 complex. We found that bone marrow-derived macrophages from Dectin-3-deficient mice were severely defective in the induction of Mincle expression in response to TDM stimulation. This defect is correlated with the failure of TDM-induced NF-κB activation in Dectin-3-deficient bone marrow-derived macrophages. Consistently, inhibition of NF-κB, but not NFAT, impaired TDM-induced Mincle expression, whereas NF-κB, but not NFAT, binds to the Mincle promoter. Dectin-3-mediated NF-κB activation is dependent on the CARD9-Bcl10-MALT1 complex. Finally, mice deficient for Dectin-3 or CARD9 produced much less proinflammatory cytokines and keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH)-specific antibodies after immunization with an adjuvant containing TDM. Overall, this study provides the mechanism by which Dectin-3 induces Mincle expression in response to Mycobacterium infection, which will have significant impact to improve adjuvant and design vaccine for antimicrobial infection.
Keywords: Innate Immunity; Lectin; NF-kappa B (NF-κB); NF-κB Transcription Factor; Signal Transduction.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Netea M. G., Brown G. D., Kullberg B. J., Gow N. A. (2008) An integrated model of the recognition of Candida albicans by the innate immune system. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 67–78 - PubMed
-
- Vautier S., MacCallum D. M., Brown G. D. (2012) C-type lectin receptors and cytokines in fungal immunity. Cytokine 58, 89–99 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

