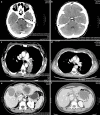
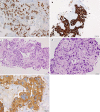
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutated Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung? A Case Report
- PMID: 25202262
- PMCID: PMC4154195
- DOI: 10.1159/000365413
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutated Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Lung? A Case Report
Abstract
Large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) of the lung is a high-grade carcinoma belonging to the neuroendocrine tumors of the lung and is different from typical lung large-cell carcinoma. It represents about 3% of all pulmonary malignancies and is characterized by neuroendocrine cytologic features. The treatment usually is platinum-based chemotherapy, however the outcome remains poor. Therefore new therapeutic options are needed. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors have demonstrated greater efficacy and better tolerability than standard chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. EGFR gene mutations were also rarely identified in LCNEC. We report a patient with lung LCNEC activating EGFR mutations who showed an impressive response to gefitinib.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation; Gefitinib; Large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma; Tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Figures
References
-
- Costanzo R, Montanino A, Di Maio M, Piccirillo MC, Sandomenico C, Giordano P, Daniele G, Franco R, Perrone F, Rocco G, Normanno N, Morabito A. Advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: current evidence and future perspectives. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2013;13:1207–1218. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Araki J, Okamoto I, Suto R, Ichikawa Y, Sasaki J. Efficacy of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib in a patient with metastatic small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2005;48:141–144. - PubMed
-
- Okamoto I, Araki J, Suto R, Shimada M, Nakagawa K, Fukuoka M. EGFR mutation in gefitinib-responsive small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2006;17:1028–1029. - PubMed
-
- Hiroshima K, Iyoda A, Shida T, Shibuya K, Iizasa T, Kishi H, Tanizawa T, Fujisawa T, Nakatani Y. Distinction of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma from small cell lung carcinoma: a morphological, immunohistochemical, and molecular analysis. Mod Pathol. 2006;19:1358–1368. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous