n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation enhances hippocampal functionality in aged mice
- PMID: 25202271
- PMCID: PMC4142709
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00220
n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation enhances hippocampal functionality in aged mice
Abstract
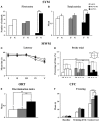
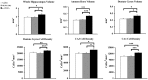
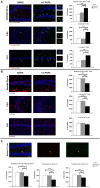
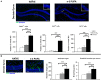
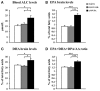
As major components of neuronal membranes, omega-3 polyunsaturated acids (n-3 PUFA) exhibit a wide range of regulatory functions, modulating from synaptic plasticity to neuroinflammation, from oxidative stress to neuroprotection. Recent human and animal studies indicated the n-3 PUFA neuroprotective properties in aging, with a clear negative correlation between n-3 PUFA levels and hippocampal deficits. The present multidimensional study was aimed at associating cognition, hippocampal neurogenesis, volume, neurodegeneration and metabolic correlates to verify n-3 PUFA neuroprotective effects in aging. To this aim 19 month-old mice were given n-3 PUFA mixture, or olive oil or no dietary supplement for 8 weeks during which hippocampal-dependent mnesic functions were tested. At the end of behavioral testing morphological and metabolic correlates were analyzed. n-3 PUFA supplemented aged mice exhibited better object recognition memory, spatial and localizatory memory, and aversive response retention, without modifications in anxiety levels in comparison to controls. These improved hippocampal cognitive functions occurred in the context of an enhanced cellular plasticity and a reduced neurodegeneration. In fact, n-3 PUFA supplementation increased hippocampal neurogenesis and dendritic arborization of newborn neurons, volume, neuronal density and microglial cell number, while it decreased apoptosis, astrocytosis and lipofuscin accumulation in the hippocampus. The increased levels of some metabolic correlates (blood Acetyl-L-Carnitine and brain n-3 PUFA concentrations) found in n-3 PUFA supplemented mice also pointed toward an effective neuroprotection. On the basis of the present results n-3 PUFA supplementation appears to be a useful tool in health promotion and cognitive decline prevention during aging.
Keywords: aging; cognitive decline; hippocampus; neuroprotection; omega-3 fatty acids.
Figures

References
-
- Abdul H. M., Calabrese V., Calvani M., Butterfield D. A. (2006). Acetyl-L-carnitine-induced up-regulation of heat shock proteins protects cortical neurons against amyloid-beta peptide 1-42-mediated oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 84, 398–408 10.1002/jnr.20877 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barhwal K., Hota S. K., Jain V., Prasad D., Singh S. B., Ilavazhagan G. (2009). Acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) prevents hypobaric hypoxia-induced spatial memory impairment through extracellular related kinase-mediated nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 phosphorylation. Neuroscience 161, 501–514 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.02.086 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonomini M., Di Liberato L., Del Rosso G., Stingone A., Marinangeli G., Consoli A., et al. (2013). Effect of an L-Carnitine containing peritoneal dialysate on insulin sensitivity in patients treated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a 4-month prospective multicenter randomized trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 62, 929–938 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.04.007 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

