Lipid regulation of BK channel function
- PMID: 25202277
- PMCID: PMC4141547
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00312
Lipid regulation of BK channel function
Abstract
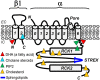
This mini-review focuses on lipid modulation of BK (MaxiK, BKCa) current by a direct interaction between lipid and the BK subunits and/or their immediate lipid environment. Direct lipid-BK protein interactions have been proposed for fatty and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, phosphoinositides and cholesterol, evidence for such action being less clear for other lipids. BK α (slo1) subunits are sufficient to support current perturbation by fatty and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, glycerophospholipids and cholesterol, while distinct BK β subunits seem necessary for current modulation by most steroids. Subunit domains or amino acids that participate in lipid action have been identified in a few cases: hslo1 Y318, cerebral artery smooth muscle (cbv1) R334,K335,K336, cbv1 seven cytosolic CRAC domains, slo1 STREX and β1 T169,L172,L173 for docosahexaenoic acid, PIP2, cholesterol, sulfatides, and cholane steroids, respectively. Whether these protein motifs directly bind lipids or rather transmit the energy of lipid binding to other areas and trigger protein conformation change remains unresolved. The impact of direct lipid-BK interaction on physiology is briefly discussed.
Keywords: MaxiK channel; electrophysiology; lipids; protein receptor site; protein-lipid interaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The steroid interaction site in transmembrane domain 2 of the large conductance, voltage- and calcium-gated potassium (BK) channel accessory β1 subunit.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 13;108(50):20207-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112901108. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22123969 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and PIP2 Modulation of BKCa Channels.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1422:217-243. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-21547-6_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36988883 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motifs in cytosolic C tail of Slo1 subunit determine cholesterol sensitivity of Ca2+- and voltage-gated K+ (BK) channels.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 8;287(24):20509-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.356261. Epub 2012 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22474334 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Ca2+-Sensitive K+ Channels by Cholesterol and Bile Acids via Distinct Channel Subunits and Sites.Curr Top Membr. 2017;80:53-93. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Curr Top Membr. 2017. PMID: 28863822 Review.
-
Central role of the BK channel in urinary bladder smooth muscle physiology and pathophysiology.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):R571-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00142.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24990859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol Regulates BK Surface Expression via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.J Neurosci. 2016 Oct 12;36(41):10625-10639. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0491-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27733613 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of calcium- and voltage-gated potassium channels of large conductance by leukotriene B4.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35314-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.577825. Epub 2014 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25371198 Free PMC article.
-
BK channels mediate a presynaptic form of mGluR-LTD in the neonatal hippocampus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 14;122(2):e2411506122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2411506122. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39773031 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium- and voltage-gated BK channels in vascular smooth muscle.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Sep;470(9):1271-1289. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2151-y. Epub 2018 May 11. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29748711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two distinct effects of PIP2 underlie auxiliary subunit-dependent modulation of Slo1 BK channels.J Gen Physiol. 2015 Apr;145(4):331-43. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201511363. J Gen Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25825171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn D. S., Kim Y. B., Lee Y. H., Kang B. S., Kang D. H. (1994). Fatty acids directly increase the activity of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in rabbit coronary smooth muscle cells. Yonsei Med. J. 35, 10–24 - PubMed
-
- Archer S. L., Gragasin F. S., Wu X., Wang S., McMurtry S., Kim D. H., et al. (2003). Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in human internal mammary artery is 11,12-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid and causes relaxation by activating smooth muscle BK(Ca) channels. Circulation 107, 769–776 10.1161/01.CIR.0000047278.28407.C2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basit S. (2013). Vitamin D in health and disease: a literature review. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 70, 161–172 - PubMed
-
- Benoit C., Renaudon B., Salvail D., Rousseau E. (2001). EETs relax airway smooth muscle via an EpDHF effect: BK(Ca) channel activation and hyperpolarization. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 280, L965–L973 - PubMed
-
- Benyahia C., Boukais K., Gomez I., Silverstein A., Clapp L., Fabre A., et al. (2013). A comparative study of PGI2 mimetics used clinically on the vasorelaxation of human pulmonary arteries and veins, role of the DP-receptor. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 107, 48–55 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2013.07.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

