The utilization of imaging features in the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms
- PMID: 25202326
- PMCID: PMC4151493
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/765451
The utilization of imaging features in the management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms
Abstract
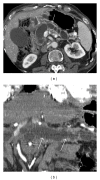
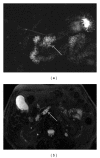
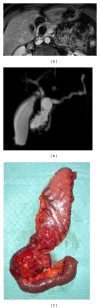
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) represent a group of cystic pancreatic neoplasms with large range of clinical behaviours, ranging from low-grade dysplasia or borderline lesions to invasive carcinomas. They can be grouped into lesions originating from the main pancreatic duct, main duct IPMNs (MD-IPMNs), and lesions which arise from secondary branches of parenchyma, denominated branch-duct IPMNs (BD-IPMNs). Management of these cystic lesions is essentially based on clinical and radiological features. The latter have been very well described in the last fifteen years, with many studies published in literature showing the main radiological features of IPMNs. Currently, the goal of imaging modalities is to identify "high-risk stigmata" or "worrisome feature" in the evaluation of pancreatic cysts. Marked dilatation of the main duct (>1 cm), large size (3-5 cm), and intramural nodules have been associated with increased risk of degeneration. BD-IPMNs could be observed as microcystic or macrocystic in appearance, with or without communication with main duct. Their imaging features are frequently overlapped with cystic neoplasms. The risk of progression for secondary IPMNs is lower, and subsequently an imaging based follow-up is very often proposed for these lesions.
Figures
References
-
- Acar M, Tatli S. Cystic tumors of the pancreas: a radiological perspective. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 2011;17(2):143–149. - PubMed
-
- Suyama M, Ariyama H, Ogawa K. Clinical diagnosis of mucin producing pancreatic carcinoma. Tan to Sui. 1986;7:739–745.
-
- Sahani DV, Kadavigere R, Saokar A, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Brugge WR, Hahn PF. Cystic pancreatic lesions: a simple imaging-based classification system for guiding management. Radiographics. 2005;25(6):1471–1484. - PubMed
-
- Manfredi R, Mehrabi S, Motton M, et al. MR imaging and MR cholangiopancreatography of multifocal intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the side branches: MR pattern and its evolution. Radiologia Medica. 2008;113(3):414–428. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

