Quantitative histopathological assessment of ocular surface squamous neoplasia using digital image analysis
- PMID: 25202353
- PMCID: PMC4156187
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2366
Quantitative histopathological assessment of ocular surface squamous neoplasia using digital image analysis
Abstract
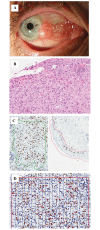
The aim of this retrospective pilot study was to evaluate the Aperio nuclear V9 algorithm as an image analysis tool to observe the histopathological changes of ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN). A histopathological assessment, including the Ki-67 proliferative index (PI) of immunohistochemically-stained tumor conjunctiva (TC) and healthy conjunctiva (HC) tissues, was performed in six cases of OSSN. The Aperio V9 algorithm was applied to digital images of the tissue specimens to count the Ki-67 PI and to measure the nuclear area indices. This digital algorithm was validated using stereological and visual analysis methods. The visual scoring of Ki-67 PI ranged from 22 to 60% (mean, 38.5%), and from 5 to 20% (mean 9.5%) in TC and HC tissue, respectively. The computer-aided analysis, using the Aperio nuclear V9 algorithm, revealed that the Ki-67 PI ranged from 21.5 to 43.5% (mean, 33.6%), and from 1.9 to 21.0% (mean, 11.8%) in the TC and HC tissue, respectively. The stereological method demonstrated that the Ki-67 PI ranged from 30.1 to 51.5% (mean, 41.0%), and from 3.2 to 30.1% (mean, 15.1%) in the TC and HC tissues, respectively. The strongest association in the collinearity of regression analysis was observed between the Aperio nuclear V9 algorithm/stereological models in the TC tissue (r2=0.7; P=0.04) and the HC tissue (r2=0.7; P=0.03), and the visual/stereological models in the TC tissue (r2=0.7; P=0.04) and the visual/Aperio nuclear V9 algorithm models in the HC tissue (r2=0.7; P=0.04). A weak and statistically insignificant association was identified between the visual/Aperio nuclear V9 algorithm analysis in the TC tissue (r2=0.4; P=0.2) and the visual/stereological models in the HC tissue (r2=0.5; P=0.13). No significant difference was observed between the nuclear area of the TC (mean, 36.5 μm2) and HC (mean, 35.7 μm2; P=0.88) tissues. It was concluded that the Aperio nuclear V9 algorithm is a useful tool for the reliable analysis of histopathological changes of OSSN. The results of this computer-aided algorithm correlate strongly with the stereological method when assessing the Ki-67 PI.
Keywords: Ki-67; digital image analysis; ocular surface squamous neoplasia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Histopathology manifestation and imaging characteristics of in vivo confocal microscopy for diagnosis of ocular surface squamous neoplasia].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Sep 11;54(9):652-660. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2018.09.004. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30220179 Chinese.
-
Sporadic Gastric Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors Have a Higher Ki-67 Proliferative Index.Endocr Pathol. 2016 Sep;27(3):259-67. doi: 10.1007/s12022-016-9443-6. Endocr Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27306997
-
Interferon Alfa 2b for Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia: Factors Influencing the Treatment Response.Semin Ophthalmol. 2019;34(7-8):465-472. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2019.1648691. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Semin Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31370766
-
A methodology to ensure and improve accuracy of Ki67 labelling index estimation by automated digital image analysis in breast cancer tissue.Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16(2):R35. doi: 10.1186/bcr3639. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24708745 Free PMC article.
-
Novel automated non invasive detection of ocular surface squamous neoplasia using multispectral autofluorescence imaging.Ocul Surf. 2019 Jul;17(3):540-550. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Ocul Surf. 2019. PMID: 30904597
References
-
- Rojo MG, Bueno G, Slodkowska J. Review of imaging solutions for integrated quantitative immunohistochemistry in the Pathology daily practice. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2009;47:349–354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
