miR-449a and CDK6 in gastric carcinoma
- PMID: 25202363
- PMCID: PMC4156198
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2370
miR-449a and CDK6 in gastric carcinoma
Abstract
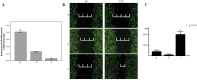
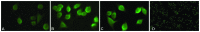
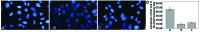
The present study aimed to identify the association between microRNA (miR/miRNA)-449a, the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)6 protein and gastric carcinoma, and discuss the effect of miR-449a on the expression of the CDK6 protein. Quantitative (q)PCR and western blot analysis were used to analyze the expression of the miR-449a and the CDK6 protein in gastric carcinoma and tumor-adjacent normal tissues. The real-time cell analyzer and the DAPI staining test were used to monitor the different miR-449a levels regulating the proliferation and apoptosis of the MGC-803 cell line. Immunofluorescence and western blot analyses were used to detect the expression level of the CDK6 protein in the cells of the miR-449a upregulation and downregulation groups, and a control group. A scratch test was used to study the effects of miR-449a expression on migration and invasion. It was found that the expression of miR-449a was downregulated and the expression of CDK6 protein was upregulated in gastric carcinoma tissue. The level of MGC-803 cell proliferation was decreased and the apoptosis level was increased by the upregulation of miR-449a expression, and the opposite effect was shown by the downregulation of expression. The expression of the CDK6 protein in the MGC-803 cells was downregulated by upregulating the expression of miR-449a. The distance of the scratch was shortened markedly after 12 h by downregulating the expression of miR-449a in the MGC-803 cells. The present study identified that a lower expression level of miR-449 and a higher expression level of CDK6 may contribute to the occurrence and development of gastric cancer. Furthermore, it was shown that miR-449a is able to regulate the expression of the CDK6 protein.
Keywords: MGC-803; cyclin-dependent kinase 6 protein; gastric carcinoma; microRNA-449; real-time cell analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
miR-449a Regulates proliferation and chemosensitivity to cisplatin by targeting cyclin D1 and BCL2 in SGC7901 cells.Dig Dis Sci. 2014 Feb;59(2):336-45. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2923-3. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Dig Dis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24248414
-
[miR-449a/b negatively regulates E2F1 to suppress proliferation of gastric cancer cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Jan 30;40(1):13-19. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.01.03. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32376557 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Effects of miR-449a on proliferation and migration of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 8;33(6):508-513. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5601.2017.121. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29931899 Chinese.
-
Negative regulation of CDK6 expression by microRNA-126-5p and its influence on the proliferation and invasion of esophageal cancer cells.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020 Nov;303(11):2811-2820. doi: 10.1002/ar.24362. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 31916689
-
microRNA-449a functions as a tumor-suppressor in gastric adenocarcinoma by targeting Bcl-2.Oncol Lett. 2013 Dec;6(6):1713-1718. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1609. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 24260067 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MiR-449a regulates autophagy to inhibit silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis through targeting Bcl2.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Nov;94(11):1267-1279. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1441-0. Epub 2016 Jun 28. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27351886
-
miR-449a: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer and Other Diseases.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1629-1650. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01322-9. Epub 2024 May 29. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38809350 Review.
-
LncRNA SNHG7 sponges miR-449a to promote pituitary adenomas progression.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Jan;36(1):123-132. doi: 10.1007/s11011-020-00611-5. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 32880813
-
miRNA-449a is downregulated in osteosarcoma and promotes cell apoptosis by targeting BCL2.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(10):8221-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3568-y. Epub 2015 May 23. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 26002578
-
Interactions between polymorphisms in the 3'untranslated region of the cyclin dependent kinase 6 gene and the human papillomavirus infection, and risk of cervical precancerous lesions.Biomed Rep. 2017 Jun;6(6):640-648. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.898. Epub 2017 May 3. Biomed Rep. 2017. PMID: 28584635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, et al. MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: a new player enters the game. Oncogene. 2010;29:5761–5771. - PubMed
-
- Lizé M, Klimke A, Dobbelstein M. MicroRNA-449 in cell fate determination. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:2874–2882. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
