Interfering with CXCR4 expression inhibits proliferation, adhesion and migration of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells
- PMID: 25202367
- PMCID: PMC4156168
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2323
Interfering with CXCR4 expression inhibits proliferation, adhesion and migration of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells
Abstract
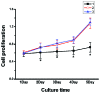
To investigate the effect and mechanism of the CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) in the proliferation and migration of breast cancer, a short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) eukaryotic expression vector targeting CXCR4 was constructed, and the impact of such on the proliferation, adhesion and migration of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells was observed. The fragments of CXCR4-shRNA were synthesized and cloned into a pGCsi-U6-Neo-green fluorescent protein vector. The recombinant plasmids were transfected into 293T cells and the most efficacious interfering vector was selected. MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected by liposome assay. The effects of silencing CXCR4 expression by shRNA on the growth, adhesion and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells were determined by Cell Counting Kit-8, cell-matrix adhesion and wound-healing assays. The shRNA eukaryotic expression vectors targeting CXCR4 (CXCR4-shRNA) were successfully constructed and transfected into 293T cells. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis revealed that the maximum inhibitory rate of CXCR4 expression was 81.3%. CXCR4-shRNA transfection significantly inhibited the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells (P<0.05), as well as the adhesion between MDA-MB-231 cells and the extracellular matrix (P<0.05). Furthermore, wound-healing assays demonstrated that the migration distance of MDA-MB-231 cells in the CXCR4-shRNA transfection group was significantly smaller than that in the control plasmid and blank control groups (P<0.01). The CXCR4-shRNA interfering vector specifically inhibited CXCR4 expression, as well as the proliferation, adhesion and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells.
Keywords: CXC chemokine receptor 4; RNA interference; breast cancer.
Figures


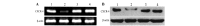
Similar articles
-
Genetic manipulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 attests the pivotal role of the autocrine SDF-1-CXCR4 pathway in the aggressiveness of breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2005 May;26(5):1429-34. Int J Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15809737
-
[Chemokine receptor CXCR4 gene silencing with shRNA inhibits breast cancer metastasis to the lung in nude mice].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2008 May;30(5):325-9. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18953828 Chinese.
-
[Construction of HSP47-shRNA and its impact on HSP47 at cellular level].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;32(4):258-63. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25518587 Chinese.
-
ShRNA-mediated gene silencing of MTA1 influenced on protein expression of ER alpha, MMP-9, CyclinD1 and invasiveness, proliferation in breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 in vitro.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011 May 19;30(1):60. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-60. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21595884 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of ANXA3 expression by RNA interference inhibits the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jan;37(1):388-398. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5251. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 27878264
Cited by
-
LY333531, a PKCβ inhibitor, attenuates glomerular endothelial cell apoptosis in the early stage of mouse diabetic nephropathy via down-regulating swiprosin-1.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Jul;38(7):1009-1023. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.172. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28414198 Free PMC article.
-
The autocrine CXCR4/CXCL12 axis contributes to lung fibrosis through modulation of lung fibroblast activity.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Mar;19(3):1844-1854. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8433. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32104240 Free PMC article.
-
Germline stem cells in human.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Oct 2;7(1):345. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01197-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36184610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCR4/CXCL12 blockade therapy; a new horizon in TNBC therapy.Med Oncol. 2025 Apr 11;42(5):161. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02705-5. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40216617 Review.
-
RTN3 Regulates the Expression Level of Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 and is Required for Migration of Primordial Germ Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 8;17(4):382. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040382. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27070582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sellers TA. Genetic factors in the pathogenesis of breast cancer: their role and relative importance. J Nutr. 1997;27(5 Suppl):929S–932S. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(Suppl 4):S3–S8. - PubMed
-
- Kulbe H, Levinson NR, Balkwill F, Wilson JL. The chemokine network in cancer - much more than directing cell movement. Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48:489–496. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
