Overexpression of c-Met increases the tumor invasion of human prostate LNCaP cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 25202379
- PMCID: PMC4156182
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2014.2390
Overexpression of c-Met increases the tumor invasion of human prostate LNCaP cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
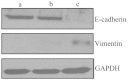
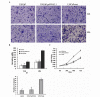
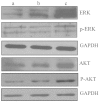
c-Met is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor that may be activated by hepatocyte growth factor, an inducer of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), to regulate the associated downstream gene expression. This process is critical to cell migration in normal and pathological conditions. In the present study, the function of c-Met in the process of EMT was investigated in prostate cancer. Initially, a c-Met stable expression cell line was constructed using EMT- and c-Met-negative LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Following the identification of c-Met in the transfected cells, the changes in EMT, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway biomarkers were determined by western blot analysis. MTT, soft agar and Transwell assays, and xenograft studies were used to investigate the effects of c-Met on the proliferation, migration and tumorigenicity of LNCaP cells. The results of the present study revealed downregulation of E-cadherin and upregulation of vimentin in LNCaP-Met cells. The results demonstrated that c-Met enhanced proliferation, migration and tumorigenicity capacity when compared with LNCaP and LNCaP-pcDNA3.1 cells. Furthermore, these EMT-like changes were mediated via the PI3K and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. The present study clearly demonstrates a crucial function for c-Met in EMT development in prostate cancer. c-Met-targeted treatment may be an effective adjuvant therapy for improving survival rates in patients with prostate cancer.
Keywords: c-Met; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; invasive potency; prostate cancer.
Figures

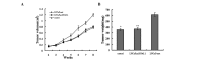
Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte growth factor increases the invasive potential of PC-3 human prostate cancer cells via an ERK/MAPK and Zeb-1 signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2016 Jan;11(1):753-759. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3943. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26870279 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostate cancer induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha.Int J Urol. 2007 Nov;14(11):1034-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2007.01866.x. Int J Urol. 2007. PMID: 17956532
-
Upregulation of long non-coding RNA PlncRNA-1 promotes proliferation and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):26090-26099. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15318. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28212533 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induces the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostatecancer cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2006 May 5;119(9):713-8. Chin Med J (Engl). 2006. PMID: 16701010
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Prostate Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1095:101-110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-95693-0_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30229551 Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin reverses the doxorubicin resistance of prostate cancer cells by downregulating the expression of c-met.Oncol Lett. 2018 Feb;15(2):2252-2258. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7561. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29434932 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting c-Met in the treatment of urologic neoplasms: Current status and challenges.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 7;13:1071030. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1071030. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36959792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A viral microRNA downregulates metastasis suppressor CD82 and induces cell invasion and angiogenesis by activating the c-Met signaling.Oncogene. 2017 Sep 21;36(38):5407-5420. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.139. Epub 2017 May 22. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28534512 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-34a and miR-206 act as novel prognostic and therapy biomarkers in cervical cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2017 Jun 9;17:63. doi: 10.1186/s12935-017-0431-9. eCollection 2017. Cancer Cell Int. 2017. PMID: 28615991 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitizing effect of c-Met kinase inhibitor BPI-9016M in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Dec;9(24):1799. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6586. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 35071493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ponzetto C, Bardelli A, Zhen Z, et al. A multifunctional docking site mediates signaling and transformation by the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor family. Cell. 1994;77:261–271. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C, Gherardi E. Developmental roles of HGF/SF and its receptor, the c-Met tyrosine kinase. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:404–410. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
