LAT-1 based primary breast cancer detection by [99m]Tc-labeled DTPA-bis-methionine scintimammography: first results using indigenously developed single vial kit preparation
- PMID: 25203145
- PMCID: PMC4158983
- DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2014.1655
LAT-1 based primary breast cancer detection by [99m]Tc-labeled DTPA-bis-methionine scintimammography: first results using indigenously developed single vial kit preparation
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic utility of a single vial ready to label with [99m]Tc kit preparation of DTPA-bis-methionine (DTPA-bis-MET) for the detection of primary breast cancer.
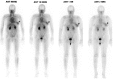
Methods: The conjugate (DTPA-bis-MET) was synthesized by covalently conjugating two molecules of methionine to DTPA and formulated as a single vial ready to label with [99m]Tc lyophilized kit preparations. Thirty female patients (mean age=47.5±11.8 years; range=21-69 years) with radiological/clinical evidence of having primary breast carcinoma were subjected to [99m]Tc-methionine scintigraphy. The whole body (anterior and posterior) imaging was performed on all the patients at 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours following an intravenous administration of 555-740 MBq radioactivity of [99m]Tc-methionine. In addition, scintimammography (static images; 256×256 matrix) at 1, 2, and 4 hours was also performed on all the patients.
Results: The resultant radiolabel, that is, [99m]Tc-DTPA-bis-MET, yielded high radiolabeling efficiency (>97.0%), radiochemical purity (166-296 MBq/μmol), and shelf life (>3 months). The radiotracer primarily gets excreted through the kidneys and localizes in the breast cancer lesions with high target-to-nontarget ratios. The mean±SD ratios on the scan-positive lesions acquired at 1, 2, and 4 hours postinjection were 3.6±0.48, 3.10±0.24, and 2.5±0.4, respectively. [99m]Tc-methionine scintimammography demonstrated an excellent sensitivity and positive predictive value of 96.0% each for the detection of primary breast cancer.
Conclusion: Ready to label single vial kit formulations of DTPA-bis-MET can be easily synthesized as in-house production and conveniently used for the scintigraphic detection of breast cancer and other methionine-dependent tumors expressing the L-type amino acid transporter-1 receptor. The imaging technique thus could be a potential substitute for the conventional single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)-based tumor imaging agents, especially for tracers with nonspecific mitochondrial uptake. However, the diagnostic efficacy of [99m]Tc-methionine needs to be evaluated in a large cohort of patients through further multicentric trials.
Keywords: [99m]Tc-methionine; breast scintimammography; cancer; single vial kit.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preclinical and Clinical Use of Indigenously Developed 99mTc-Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid-Bis-Methionine: l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1-Targeted Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Radiotracer for Glioma Management.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Aug 3;6(9):1233-1247. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00091. eCollection 2023 Sep 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37705592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of specific SPECT-radiopharmaceutical for tumor imaging based on methionine: 99mTc-DTPA-bis(methionine).Bioconjug Chem. 2010 Feb 17;21(2):229-39. doi: 10.1021/bc900197n. Bioconjug Chem. 2010. PMID: 20108938
-
Kit preparation and biokinetics in women of 99mTc-EDDA/HYNIC-E-[c(RGDfK)]2 for breast cancer imaging.Nucl Med Commun. 2014 Apr;35(4):423-32. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000065. Nucl Med Commun. 2014. PMID: 24335877
-
Comparative evaluation of glutamate-sensitive radiopharmaceuticals: Technetium-99m-glutamic acid and technetium-99m-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid-bis(glutamate) conjugate for tumor imaging.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2010 Dec;25(6):645-55. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2010.0848. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2010. PMID: 21204758
-
The role of nuclear medicine in breast cancer detection: a focus on Technetium-99 Sestamibi scintimammography.Curr Oncol Rep. 2003 Jan;5(1):58-62. doi: 10.1007/s11912-003-0087-6. Curr Oncol Rep. 2003. PMID: 12493151 Review.
Cited by
-
Amino Acid Metabolism as a Target for Breast Cancer Imaging.PET Clin. 2018 Jul;13(3):437-444. doi: 10.1016/j.cpet.2018.02.009. PET Clin. 2018. PMID: 30100081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Amino Acids in the Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, and Treatment of Breast Cancer: A Review.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Sep 13;45(9):7513-7537. doi: 10.3390/cimb45090474. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37754258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amino acid metabolism in breast cancer: pathogenic drivers and therapeutic opportunities.Protein Cell. 2025 Jul 19;16(7):506-531. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwaf011. Protein Cell. 2025. PMID: 39973065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Discovery by Molecular Imaging and Monitoring Therapy Response in Lymphoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 27;18(8):1639. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081639. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28749424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical and Clinical Use of Indigenously Developed 99mTc-Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid-Bis-Methionine: l-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1-Targeted Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Radiotracer for Glioma Management.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Aug 3;6(9):1233-1247. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00091. eCollection 2023 Sep 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37705592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buist DSM, Porter PL, Lehman C, et al. . Factors contributing to mammography failure in women aged 40–49 years. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004;96:1432. - PubMed
-
- Coates AS, Keshaviah A, Thürlimann B, et al. . Five years of letrozole compared with tamoxifen as initial adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: Update of study BIG 1–98. J Clin Oncol 2007;25:486. - PubMed
-
- Giordano SH. Update on locally advanced breast cancer. Oncologist 2003;8:521. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

