Multimodal imaging for improved diagnosis and treatment of cancers
- PMID: 25204551
- PMCID: PMC4352132
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.29012
Multimodal imaging for improved diagnosis and treatment of cancers
Abstract
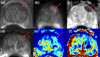
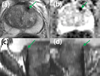
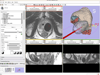
The authors review methods for image-guided diagnosis and therapy that increase precision in the detection, characterization, and localization of many forms of cancer to achieve optimal target definition and complete resection or ablation. A new model of translational, clinical, image-guided therapy research is presented, and the Advanced Multimodality Image-Guided Operating (AMIGO) suite is described. AMIGO was conceived and designed to allow for the full integration of imaging in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Examples are drawn from over 500 procedures performed on brain, neck, spine, thorax (breast, lung), and pelvis (prostate and gynecologic) areas and are used to describe how they address some of the many challenges of treating brain, prostate, and lung tumors. Cancer 2015;121:817-827. © 2014 American Cancer Society.
Keywords: brain tumor; interventional magnetic resonance imaging; intraoperative monitoring; lung cancer; mass spectroscopy; multimodal imaging; neuroimaging; neuronavigation; prostate biopsy; prostate cancer.
© 2014 American Cancer Society.
Figures







References
-
- Jolesz FA. Intraoperative Imaging and Image-Guided Therapy. Springer London: Limited; 2013.
-
- Tatli S, et al. Abdominal masses sampled at PET/CT-guided percutaneous biopsy: initial experience with registration of prior PET/CT images. Radiology. 2010 Jul;256(1):305–311. - PubMed
-
- Sanai N, Berger MS. Glioma extent of resection and its impact on patient outcome. Neurosurgery. 2008 Apr;62(4):753–764. discussion 264–756. - PubMed
-
- Claus EB, et al. Survival rates in patients with low-grade glioma after intraoperative magnetic resonance image guidance. Cancer. 2005 Mar 15;103(6):1227–1233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R25CA089017/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA120528/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 RR019703/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA111288/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR019703/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019513/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA089017/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA120528/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA111288/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41EB015898/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA067165/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015898/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA156943/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21CA156943/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R0ICA160902-01A1/PHS HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

