Cisplatin-induced antitumor immunomodulation: a review of preclinical and clinical evidence
- PMID: 25204552
- PMCID: PMC4216745
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1298
Cisplatin-induced antitumor immunomodulation: a review of preclinical and clinical evidence
Abstract
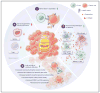
Contrary to the long held belief that chemotherapy is immunosuppressive, emerging evidence indicates that the anticancer activity of cisplatin is not limited to its ability to inhibit mitosis, but that cisplatin also has important immunomodulatory effects. We therefore methodically examined the relevant preclinical literature and identified four main mechanisms of cisplatin-induced antitumor immunomodulation: (i) MHC class I expression upregulation; (ii) recruitment and proliferation of effector cells; (iii) upregulation of the lytic activity of cytotoxic effectors; and (iv) downregulation of the immunosuppressive microenvironment. Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy's antitumor immunomodulatory effects are also beginning to be harnessed in the clinic; we therefore additionally reviewed the applicable clinical literature and discussed how monitoring various components of the immune system (and their responses to cisplatin) can add new levels of sophistication to disease monitoring and prognostication. In summation, this growing body of literature on cisplatin-induced antitumor immunomodulation ultimately highlights the therapeutic potential of synergistic strategies that combine traditional chemotherapy with immunotherapy.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Lebwohl D, Canetta R. Clinical development of platinum complexes in cancer therapy: an historical perspective and an update. Eur J Cancer. 1998;34:1522–34. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg B, Vancamp L, Krigas T. Inhibition of Cell Division in Escherichia Coli by Electrolysis Products from a Platinum Electrode. Nature. 1965;205:698–9. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg B, Van Camp L, Grimley EB, Thomson AJ. The inhibition of growth or cell division in Escherichia coli by different ionic species of platinum(IV) complexes. J Biol Chem. 1967;242:1347–52. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg B, VanCamp L, Trosko JE, Mansour VH. Platinum compounds: a new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature. 1969;222:385–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials