Central but not systemic administration of XPro1595 is therapeutic following moderate spinal cord injury in mice
- PMID: 25204558
- PMCID: PMC4176557
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-014-0159-6
Central but not systemic administration of XPro1595 is therapeutic following moderate spinal cord injury in mice
Abstract
Background: Glial cell activation and overproduction of inflammatory mediators in the central nervous system (CNS) have been implicated in acute traumatic injuries to the CNS, including spinal cord injury (SCI). Elevated levels of the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which exists in both a soluble (sol) and a transmembrane (tm) form, have been found in the lesioned cord early after injury. The contribution of solTNF versus tmTNF to the development of the lesion is, however, still unclear.
Methods: We tested the effect of systemically or centrally blocking solTNF alone, using XPro1595, versus using the drug etanercept to block both solTNF and tmTNF compared to a placebo vehicle following moderate SCI in mice. Functional outcomes were evaluated using the Basso Mouse Scale, rung walk test, and thermal hyperalgesia analysis. The inflammatory response in the lesioned cord was investigated using immunohistochemistry and western blotting analyses.
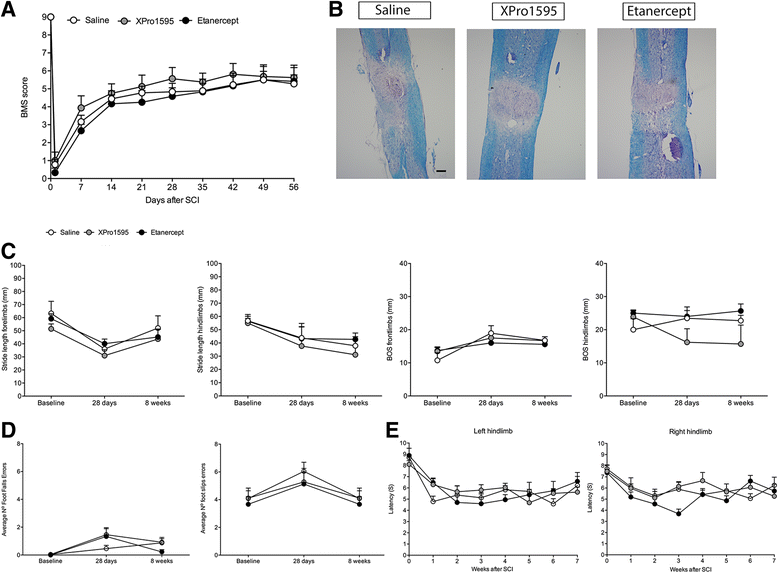
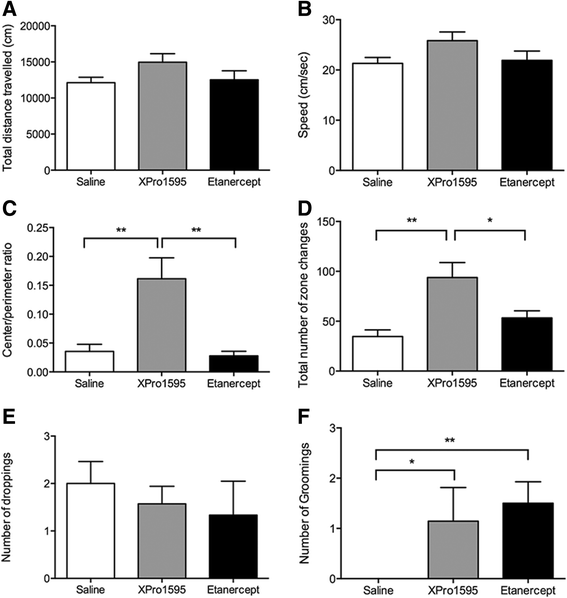
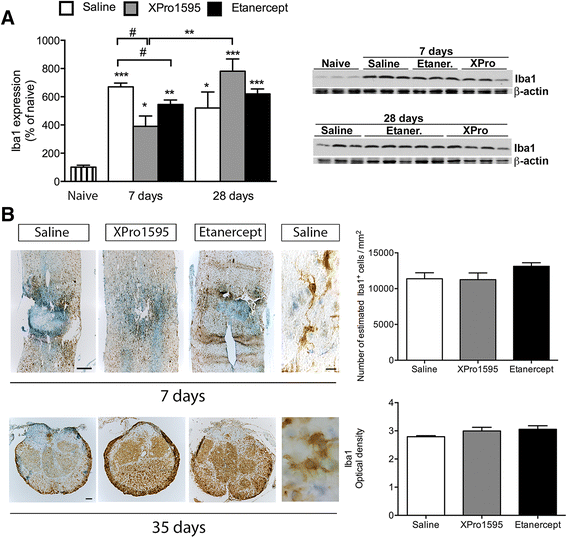
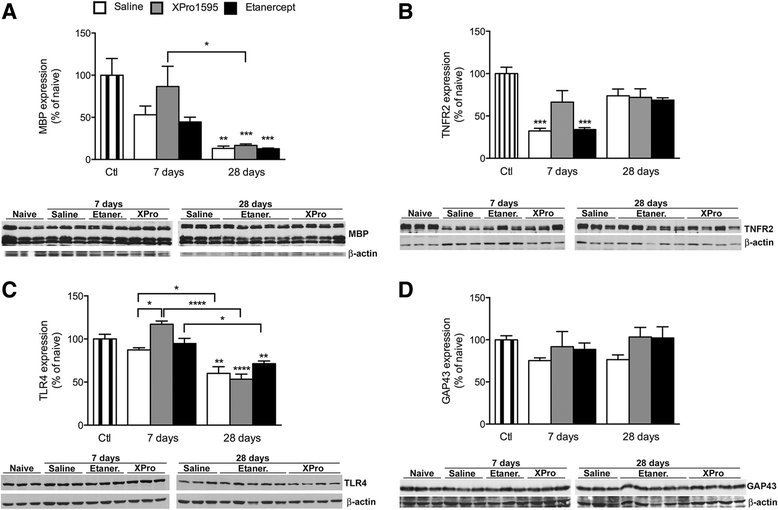
Results: We found that peripheral administration of anti-TNF therapies had no discernable effect on locomotor performances after SCI. In contrast, central administration of XPro1595 resulted in improved locomotor function, decreased anxiety-related behavior, and reduced damage to the lesioned spinal cord, whereas central administration of etanercept had no therapeutic effects. Improvements in XPro1595-treated mice were accompanied by increases in Toll-like receptor 4 and TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2) protein levels and changes in Iba1 protein expression in microglia/macrophages 7 and 28 days after SCI.
Conclusions: These studies suggest that, by selectively blocking solTNF, XPro1595 is neuroprotective when applied directly to the lesioned cord. This protection may be mediated via alteration of the inflammatory environment without suppression of the neuroprotective effects of tmTNF signaling through TNFR2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systemically administered anti-TNF therapy ameliorates functional outcomes after focal cerebral ischemia.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Dec 12;11:203. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0203-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 25498129 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Inhibition of Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Alters the Neuroinflammatory Response following Moderate Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jun 12;12(6):845. doi: 10.3390/biology12060845. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372129 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Ablation of Soluble TNF Does Not Affect Lesion Size and Functional Recovery after Moderate Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:2684098. doi: 10.1155/2016/2684098. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 28070141 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α antagonist reduces apoptosis of neurons and oligodendroglia in rat spinal cord injury.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011 Aug 1;36(17):1350-8. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181f014ec. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011. PMID: 21224756
-
TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Oct 17;5:45. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-45. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18925972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selective inhibition of soluble tumor necrosis factor signaling reduces abdominal aortic aneurysm progression.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 16;9:942342. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.942342. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36186984 Free PMC article.
-
Featured Article: Deterioration of visual function mediated by senescence-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in inflammatory tie2-TNF mice.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Aug;243(12):976-984. doi: 10.1177/1535370218794915. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 30114984 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic inhibition of soluble TNF significantly changes glial cell populations leading to improved myelin integrity and better functional outcome after experimental stroke.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Aug;189:118334. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118334. Epub 2025 Jul 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40645014 Free PMC article.
-
TNFR2 promotes Treg-mediated recovery from neuropathic pain across sexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Aug 20;116(34):17045-17050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902091116. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31391309 Free PMC article.
-
Systemically administered anti-TNF therapy ameliorates functional outcomes after focal cerebral ischemia.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Dec 12;11:203. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0203-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 25498129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bracchi-Ricard V, Lambertsen KL, Ricard J, Nathanson L, Karmally S, Johnstone J, Ellman DG, Frydel B, McTigue DM, Bethea JR. Inhibition of astroglial NF-kappaB enhances oligodendrogenesis following spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2013;10(1):92. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-10-92. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

