Estradiol and cognitive function: past, present and future
- PMID: 25205317
- PMCID: PMC4318702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.08.011
Estradiol and cognitive function: past, present and future
Abstract
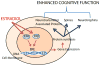
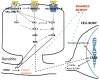
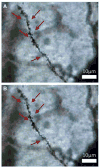
A historical perspective on estradiol's enhancement of cognitive function is presented, and research, primarily in animals, but also in humans, is reviewed. Data regarding the mechanisms underlying the enhancements are discussed. Newer studies showing rapid effects of estradiol on consolidation of memory through membrane interactions and activation of inter-cellular signaling pathways are reviewed as well as studies focused on traditional genomic mechanisms. Recent demonstrations of intra-neuronal estradiol synthesis and possible actions as a neurosteroid to promote memory are discussed. This information is applied to the critical issue of the current lack of effective hormonal (or other) treatments for cognitive decline associated with menopause and aging. Finally, the critical period hypothesis for estradiol effects is discussed along with novel strategies for hormone/drug development. Overall, the historical record documents that estradiol positively impacts some aspects of cognitive function, but effective therapeutic interventions using this hormone have yet to be realized.
Keywords: Aging; Cognition; Estradiol; Estrogen receptors; Hormone replacement therapy; Memory.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


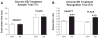



References
-
- Aggleton JP, Blindt HS, Candy JM. Working memory in aged rats. Behav Neurosci. 1989;103:975–983. - PubMed
-
- Bagger YZ, Tanko LB, Alexandersen P, Qin G, Christiansen GC PERF Study Group. Early postmenopausal hormone therapy may prevent cognitive impairment later in life. Menopause. 2005;12:12–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

