Distribution pattern of acetylcholinesterase in the optic tectum of two Indian air breathing teleosts
- PMID: 25206001
- PMCID: PMC4117095
- DOI: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200104
Distribution pattern of acetylcholinesterase in the optic tectum of two Indian air breathing teleosts
Abstract
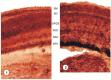
Background: A histoenzymological study has been carried out on the distribution of enzyme acetylcholinesterase in the optic tectum of two Indian air breathing teleosts by employing a histochemical technique to visualize acetylcholinesterase containing neurons described by Hedreen, JC (1985).
Purpose: Data available on enzyme localizaton in the brain of fishes, particularly Indian teleosts is inadequate and scattered.
Methods: AChE distribution in the optic tectum shows a prevalent pattern characterized by precise laminar distribution of enzyme which shows alternatively strong, weak or negative reaction in the different layers.
Results: Layers with maximum enzyme activity most likely correspond to areas where cholinergic mechanism is prevailing whereas layers with mild activity may be considered to be non-chalinergic/cholinoceptive having some cholinergic innervations from other layers.
Conclusion: The present investigation suggests some possible connections between enzyme localization and functional and anatomical organization of optic tectum.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase Optic tectum Cholinergic Stratum marginale Teleost.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None
Figures
References
-
- Soreq H, Seidman S. Acetylcholinesterase: New roles for an old actor. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;2:294–302. - PubMed
-
- Downes GB, Granto M. Acetylcholinesterase function is dispensable for sensory neurite growth but is critical for neuromuscular synapse stability. Dev Biol. 2004;70:232–245. - PubMed
-
- Silman I, Sussman JL. Acetylcholinesterase classical and non-classical functions and phramacology. Curr Opin Phermacol. 2005;5:293–302. - PubMed
-
- Chubb IW, Hodgson AJ, White CH. Acetylcholiesterase hydrolyses substance P. Neuroscience. 1980;5:2065–72. - PubMed
-
- Shute CCD, Lewis PR. Cholinesterase containing system of the brain of the rat. Nature. 1963;199:1160–1164. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources