Primary spinal primitive neuroectodermal tumour - a case report
- PMID: 25206019
- PMCID: PMC4117112
- DOI: 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200211
Primary spinal primitive neuroectodermal tumour - a case report
Abstract
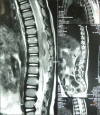
Primitive neuroectodermal tumours (PNET) are aggressive childhood malignancies and offer a significant challenge to treatment. A two years old female child presented with weakness both lower limbs. Preoperative MRI of the spine and paravertebral regionIso - hyper intense posterior placed extradural lesion, non contrast enhancing from D11-L2 levels with cord compression D9 to L3 laminectomy done. Granulation tissue found from D11 to L2. with cord compression. The granulation tissue removed in toto. The pathological findings were consistent with PNET. Post operative neurological improvement was minimal. Cranial screening ruled out any intracranialtumour. Hence a diagnosis of primary spinal PNET was made. A review of the literature shows that only 19 cases of primary intraspinal PNETs have been reported to date and the present case extradural in location. Primary intraspinal PNETs are rare tumors and carry a poor prognosis.
Keywords: Primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET); Spinal cord.
Figures
References
-
- Akgun B, Ates D, Kaplan M. Ganglioneuroblastoma of the thoracic spinal cord: a very rare case report. ActaMedica (Hradec Kralove) 2012;55(1):50–52. - PubMed
-
- Coumans JV, Walcott BP, Nahed BV et al. Multimodal therapy of an intramedullary cervical primitiveneuroectodermal tumor in an adult. J ClinOncol. 2012;30(2): - PubMed
-
- Parikh D, Short M, Eshmawy M et al. Surgical outcome analysis of paediatric thoracic and cervical neuroblastoma., Brown R. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;41(3):630–634. - PubMed
-
- Gollard RP, Rosen L, Anson J et al. Intramedullary PNET of the spine: long-term survival after combined modality therapy and subsequent relapse. J PediatrHematolOncol. 2011;33(2):107–112. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources