Cherubism: a case report
- PMID: 25206123
- PMCID: PMC4086575
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1019
Cherubism: a case report
Abstract
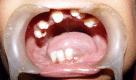
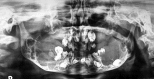
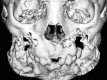
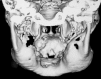
Cherubism, a pediatric disease, is a self limiting non-neoplastic autosomal dominant fibro-osseous disorder of jaws. It is a self limiting disease and rarely apparent before the age of two years. It occurs in children and predominantly in boys. It is characterized by clinical bilateral swelling of cheeks due to bony enlargement of jaws that give the patient a typical 'cherubic' look. Regression occurs during puberty when the disease stabilizes after the growth period leaving some facial deformity and malocclusion. Cherubism may occur in solitary cases or in many members of the family, often in multiple generations. Radiographically, lesion appears as bilateral multilocular radiolucent areas. Since it was first described by Jones in 1933, many cases have been documented. Here a case of 8 years old cherubic child, with his clinical appearance as well as radiological evaluation and discussion about clinical outcome are presented. The patient was diagnosed but not treated.
Keywords: Cherubism; autosomal dominant; fibro-osseous disorder; multilocular radiolucencies; multinucleated giant cells.; osteoclastic lesions; self limiting.
Figures

References
-
- Jones WA. Familial multilocular cystic disease of the jaws. Am J Cancer. 1933;17:946–950.
-
- Ueki Y, Tiziani V, Santanna C, Fukai N, Maulik C, Garfinkle J, Ninomiya C, doAmaral C, Peters H, Habal M. Mutation in the gene encoding c-abi binding protein SH3BP2 cause cherubism. Nat Genet . 2001 Jun;28(2):125–126. - PubMed
-
- Arnott DG. Cherubism- An initial unilateral presentation. Br J Oral Surg. 1978 Jul;16(1):38–46. - PubMed
-
- Pindborg JJ, Kramer IR. World Health Organization. 1st ed. Geneva: 1971. Histological typing of odontogenic tumours, jaw cysts, and allied lesions; pp. 18–19.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
