Back propagation artificial neural network for community Alzheimer's disease screening in China
- PMID: 25206598
- PMCID: PMC4107524
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.03.010
Back propagation artificial neural network for community Alzheimer's disease screening in China
Abstract
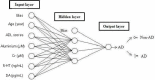
Alzheimer's disease patients diagnosed with the Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders diagnostic criteria were selected from the community through on-site sampling. Levels of macro and trace elements were measured in blood samples using an atomic absorption method, and neurotransmitters were measured using a radioimmunoassay method. SPSS 13.0 was used to establish a database, and a back propagation artificial neural network for Alzheimer's disease prediction was simulated using Clementine 12.0 software. With scores of activities of daily living, creatinine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, age, dopamine and aluminum as input variables, the results revealed that the area under the curve in our back propagation artificial neural network was 0.929 (95% confidence interval: 0.868-0.968), sensitivity was 90.00%, specificity was 95.00%, and accuracy was 92.50%. The findings indicated that the results of back propagation artificial neural network established based on the above six variables were satisfactory for screening and diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease in patients selected from the community.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; artificial neural network; clinical practice; community; grant-supported paper; mathematical model; neural regeneration; neuroregeneration; neurotransmitters; trace elements.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189–198. - PubMed
-
- Lehéricy S, Delmaire C, Galanaud D, et al. Neuroimaging in dementia. Presse Med. 2007;36(10 Pt 2):1453–1463. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien JT. Role of imaging techniques in the diagnosis of dementia. Br J Radiol. 2007;80(Spec No 2):S71–77. - PubMed
-
- Pimlott SL, Ebmeier KP. SPECT imaging in dementia. Br J Radiol. 2007;80(Spec No 2):S153–159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
