Atorvastatin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
- PMID: 25206811
- PMCID: PMC4146150
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.128220
Atorvastatin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects
Abstract
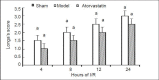
In addition to its lipid-lowering effect, atorvastatin exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects as well. In this study, we hypothesized that atorvastatin could protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. The middle cerebral artery ischemia/reperfusion model was established, and atorvastatin, 6.5 mg/kg, was administered by gavage. We found that, after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, levels of the inflammation-related factors E-selectin and myeloperoxidase were upregulated, the oxidative stress-related marker malondialdehyde was increased, and superoxide dismutase activity was decreased in the ischemic cerebral cortex. Atorvastatin pretreatment significantly inhibited these changes. Our findings indicate that atorvastatin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Keywords: E-selectin; NSFC grant; atorvastatin; blood-brain barrier; brain injury; cerebral ischemia/reperfusion; free radicals; inflammation; malondialdehyde; myeloperoxidase; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; stroke; superoxide dismutase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Barba R, Martinez-Espinosa S, Rodriguez-Garcia E, et al. Poststroke dementia: clinical features and risk factors. Stroke. 2000;31(7):1494–1501. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki T, Kimura Y, Ohata H, et al. Distinct effects of tissue-type plasminogen activator and SMTP-7 on cerebrovascular inflammation following thrombolytic reperfusion. Stroke. 2011;42:1097–1104. - PubMed
-
- DeVeber G. Arterial ischemic strokes in infants and children: an overview of current approaches. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2003;29(6):567–573. - PubMed
-
- DeVeber G. Risk factors for childhood stroke: little folks have different strokes! Ann Neurol. 2003;53(2):149–150. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
