Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 influences hippocampal neuronal survival in a rat model of diabetic cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 25206883
- PMCID: PMC4146267
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.131581
Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 influences hippocampal neuronal survival in a rat model of diabetic cerebral ischemia
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 influences hippocampal neuronal survival in a rat model of diabetic cerebral ischemia.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Nov 1;19(11):2364. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00178. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38526272 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
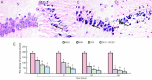
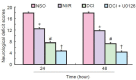
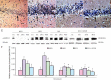
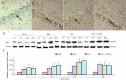
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 has been demonstrated in acute brain ischemia. We hypothesized that activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 can protect hippocampal neurons from injury in a diabetic model after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. In this study, transient whole-brain ischemia was induced by four-vessel occlusion in normal and diabetic rats, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 inhibitor (U0126) was administered into diabetic rats 30 minutes before ischemia as a pretreatment. Results showed that the number of surviving neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region was reduced, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation and Ku70 activity were decreased, and pro-apoptotic Bax expression was upregulated after intervention using U0126. These findings demonstrate that inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activity aggravated neuronal loss in the hippocampus in a diabetic rat after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion, further decreased DNA repairing ability and accelerated apoptosis in hippocampal neurons. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation plays a neuroprotective role in hippocampal neurons in a diabetic rat after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.
Keywords: Bax; DNA dependent protein kinase; apoptosis; brain injury; cerebral ischemia/reperfusion; extracellular signal-regulated kinase; hippocampus; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Remote Ischemic Postconditioning Improve Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Induced Cognitive Dysfunction through Suppressing Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Hippocampus via TK/BK/B2R-Mediated PI3K/AKT.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10652-10669. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04864-y. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40229456 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of N-acetylcysteine on apoptosis and NGF-Akt/Bad pathway in the hippocampus tissue of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in male rats.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jun 6;40(5):217. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01641-7. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40478359
-
Ershiwuwei Shanhu pills alleviates cerebral ischemia injury in rats by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress through GRP78/XBP1/CHOP pathway.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:156969. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156969. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40532596
-
Cooling for cerebral protection during brain surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 28;1(1):CD006638. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006638.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25626888 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental evaluation of clinical colon anastomotic leakage.Dan Med J. 2014 Mar;61(3):B4821. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 24814921
Cited by
-
Ku70 silencing aggravates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced injury by activation of the p53 apoptotic pathway in rat cortical astrocytes.Histochem Cell Biol. 2024 Dec 23;163(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s00418-024-02352-3. Histochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39715938
-
Retraction: Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 influences hippocampal neuronal survival in a rat model of diabetic cerebral ischemia.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Nov 1;19(11):2364. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00178. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38526272 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Activation of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 1 Enhances Hippocampus Neurogenesis in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury: An Involvement of MEK/Erk Signaling Pathway.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:8072156. doi: 10.1155/2016/8072156. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 28018679 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of blood leptin and adropin levels in patients with multiple sclerosis: A CONSORT-clinical study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Sep 17;100(37):e27247. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027247. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34664869 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Adropin as the Medium of Dialogue between Energy Regulation and Immune Regulation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 4;2020:3947806. doi: 10.1155/2020/3947806. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32190172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe K, Misawa M. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade suppresses amyloid beta protein-induced promotion of glutamate clearance in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Brain Res. 2003;1997:179–187. - PubMed
-
- Bell DS. Stroke in the diabetic patient. Diabetes Care. 1999;17:213–214. - PubMed
-
- Clausen F, Lundqvist H, Ekmark S, Lewén A, Ebendal T, Hillered L. Oxygen free radical-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase mediates apoptosis-like cell death after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:1168–1182. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
