Desferrithiocin: a search for clinically effective iron chelators
- PMID: 25207964
- PMCID: PMC4255733
- DOI: 10.1021/jm500828f
Desferrithiocin: a search for clinically effective iron chelators
Abstract
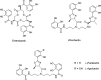
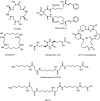
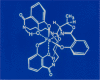
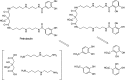
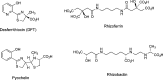
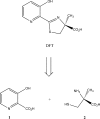
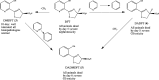
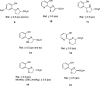
The successful search for orally active iron chelators to treat transfusional iron-overload diseases, e.g., thalassemia, is overviewed. The critical role of iron in nature as a redox engine is first described, as well as how primitive life forms and humans manage the metal. The problems that derive when iron homeostasis in humans is disrupted and the mechanism of the ensuing damage, uncontrolled Fenton chemistry, are discussed. The solution to the problem, chelator-mediated iron removal, is clear. Design options for the assembly of ligands that sequester and decorporate iron are reviewed, along with the shortcomings of the currently available therapeutics. The rationale for choosing desferrithiocin, a natural product iron chelator (a siderophore), as a platform for structure-activity relationship studies in the search for an orally active iron chelator is thoroughly developed. The study provides an excellent example of how to systematically reengineer a pharmacophore in order to overcome toxicological problems while maintaining iron clearing efficacy and has led to three ligands being evaluated in human clinical trials.
Figures
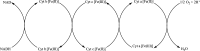

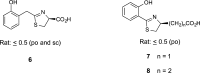
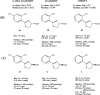
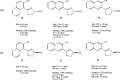
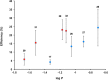

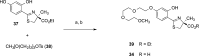
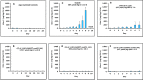
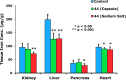
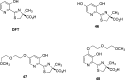
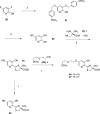
References
-
- Mladenka P.; Hrdina R.; Hübl M.; Simunek T. The Fate of Iron in the Organism and Its Regulatory Pathways. Acta Med. (Hradec Kralove, Czech Repub.) 2005, 48, 127–135. - PubMed
-
- Bauer I.; Knolker H.-J.. Iron Complexes in Organic Chemistry. In Iron Catalysis in Organic Chemistry; Plietker B., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp 1–28.
-
- Sutton H. C.; Winterbourn C. C. On the Participation of Higher Oxidation States of Iron and Copper in Fenton Reactions. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1989, 6, 53–60. - PubMed
-
- Crichton R.Inorganic Biochemistry of Iron Metabolism: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Consequences, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, 2001.
-
- Campanella L.; Capesciotti G. S.; Russo M. V.; Tomassetti M. Study of the Catalytic Mechanism of the Enzyme Catalase on Organic Hydroperoxides in Non-polar Organic Solvent. Curr. Enzyme Inhib. 2008, 4, 86–92.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

