The RNA-binding protein Staufen1 impairs myogenic differentiation via a c-myc-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 25208565
- PMCID: PMC4230783
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0895
The RNA-binding protein Staufen1 impairs myogenic differentiation via a c-myc-dependent mechanism
Abstract
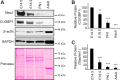
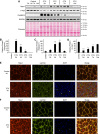
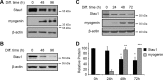
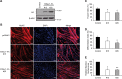
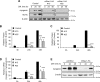
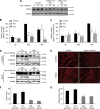
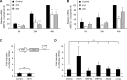
Recent work has shown that Staufen1 plays key roles in skeletal muscle, yet little is known about its pattern of expression during embryonic and postnatal development. Here we first show that Staufen1 levels are abundant in mouse embryonic muscles and that its expression decreases thereafter, reaching low levels in mature muscles. A similar pattern of expression is seen as cultured myoblasts differentiate into myotubes. Muscle degeneration/regeneration experiments revealed that Staufen1 increases after cardiotoxin injection before returning to the low levels seen in mature muscles. We next prevented the decrease in Staufen1 during differentiation by generating stable C2C12 muscle cell lines overexpressing Staufen1. Cells overexpressing Staufen1 differentiated poorly, as evidenced by reductions in the differentiation and fusion indices and decreases in MyoD, myogenin, MEF2A, and MEF2C, independently of Staufen-mediated mRNA decay. However, levels of c-myc, a factor known to inhibit differentiation, were increased in C2C12 cells overexpressing Staufen1 through enhanced translation. By contrast, the knockdown of Staufen1 decreased c-myc levels in myoblasts. Collectively our results show that Staufen1 is highly expressed during early stages of differentiation/development and that it can impair differentiation by regulating c-myc, thereby highlighting the multifunctional role of Staufen1 in skeletal muscle cells.
© 2014 Ravel-Chapuis et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures

References
-
- Amack JD, Mahadevan MS. The myotonic dystrophy expanded CUG repeat tract is necessary but not sufficient to disrupt C2C12 myoblast differentiation. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:1879–1887. - PubMed
-
- Amirouche A, Tadesse H, Lunde JA, Belanger G, Cote J, Jasmin BJ. Activation of p38 signaling increases utrophin A expression in skeletal muscle via the RNA-binding protein KSRP and inhibition of AU-rich element-mediated mRNA decay: implications for novel DMD therapeutics. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22:3093–3111. - PubMed
-
- Beauchamp P, Nassif C, Hillock S, van der Giessen K, von Roretz C, Jasmin BJ, Gallouzi IE. The cleavage of HuR interferes with its transportin-2-mediated nuclear import and promotes muscle fiber formation. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:1588–1599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

